Includes Heavy Menstrual Bleeding ( Mennorhagia ), Irregular, Intermenstrual and Post Coital Bleeding
Normal Menstrual Cycle
A “normal” menstrual cycle is defined based on 4 parameters (frequency, regularity, duration, or volume) summarised in the table below
| Parameter Normal Limits | (5th to 95th centile) |
| Frequency of menses (days) | 24 to 38 days |
| Regularity (Cycle length) | ≤7 to 9 days |
| Duration (days of bleeding in a single menstrual period) | ≤8 days |
| Volume (monthly blood loss) | Clinical definition is subjective and defined as a volume of menstrual blood loss that does not interfere with a woman’s physical, social, emotional, and/or quality of life |
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
is the overarching term used to describe any symptomatic variation from normal menstruation and also includes intermenstrual bleeding. The Table below summarises the recommended terminology for women with AUB.
| Parameters | Terminology | Out with 5th to 95th centile |
| Frequency of menses (days) | Absent | Amenorrhoea – Primary or Secondary |
| Infrequent | >38 days | |
| Frequent | <24 days | |
| Regularity (Cycle length) | Irregular | Variation >10 days – Cycle length is the number of days from the first day of one menstrual cycle to the first day of the next |
| Duration (days of bleeding in a single menstrual period) | Prolonged | > 8 days |
| Volume (monthly blood loss) | Heavy or light | Subjectively defined |
| Spontaneous bleeds occurring in between periods | Intermenstrual bleeding (IMB) | Cyclic (early, mid, late cycle) or random, Midcycle IMB may represent a nadir in estradiol levels (ovulation) and is physiological (9% of women). |
Causes – See Fig Below PALM- COEIN System to identify potential Causes of AUB
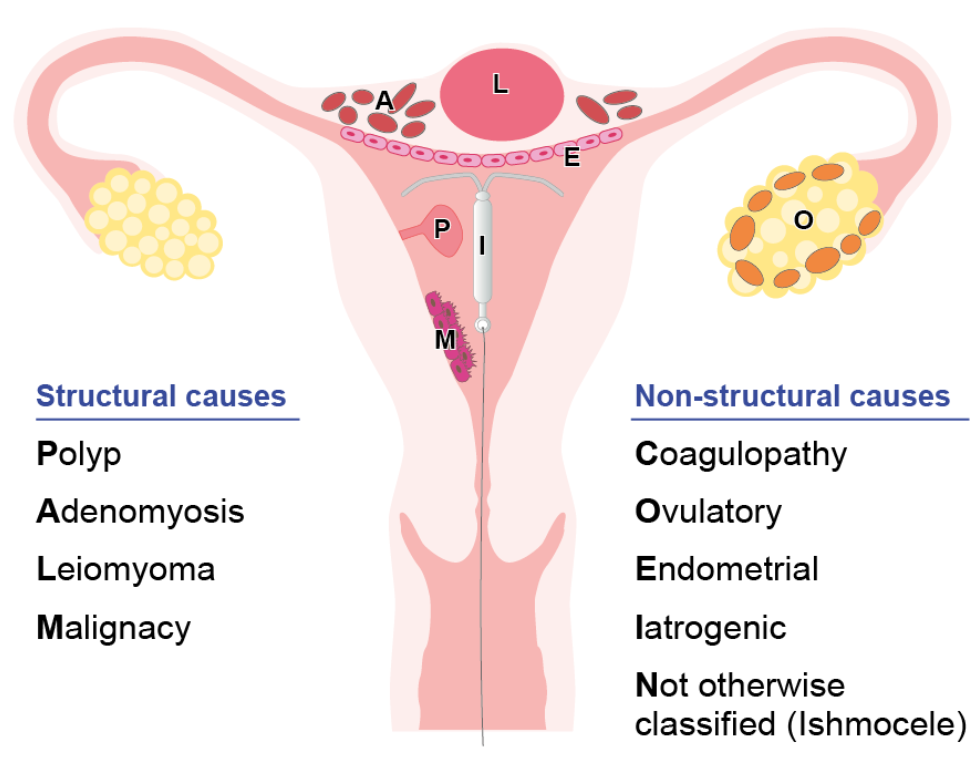
Diagram reproduced from “Biomarkers
in abnormal uterine bleeding -Rohan Chodankar, Hilary O D Critchley
Biology of Reproduction/ ioy231, https://doi.org/10.1093/biolre/ioy231
See Risk assessment for STI and Chlamydia referral guidance on the STI RefHelp page