Information:
Intermittent short lived non-positional balance disturbance is very common in all age groups and is probably multifactorial. It is not indicative of any specific or treatable pathology. It does tend to settle over a year or so. Strong reassurance is often all that is required but encourage patients to keep on moving as this helps with habituation.
ENT Balance Clinic
This is a specialised multidisciplinary clinic to investigate those who do not have BPPV and where history and examination makes an otological condition likely. Staff include
KEY MESSAGES:
Multiple studies have shown that in patients referred to Balance Clinics:
- By FAR the commonest diagnoses are BPPV and Vestibular Migraine
- Please see here for management details:
- BPPV –BPPV (Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo) (nhslothian.scot)
- Vestibular migraine – diagnosis and Advice for management of migraine in primary care (nhslothian.scot)
- A THIRD to HALF of those referred have BOTH BPPV and vestibular migraine.
- Vestibular Neuritis and central neurological causes of vertigo are associated with a minority.
ENT specialists, a specialist Vestibular Audiologist and access to a balance physiotherapist, hearing tests and other Audiology services.
According to the history and examination, it may be advisable to exclude anaemia, diabetes or thyroid disorder.
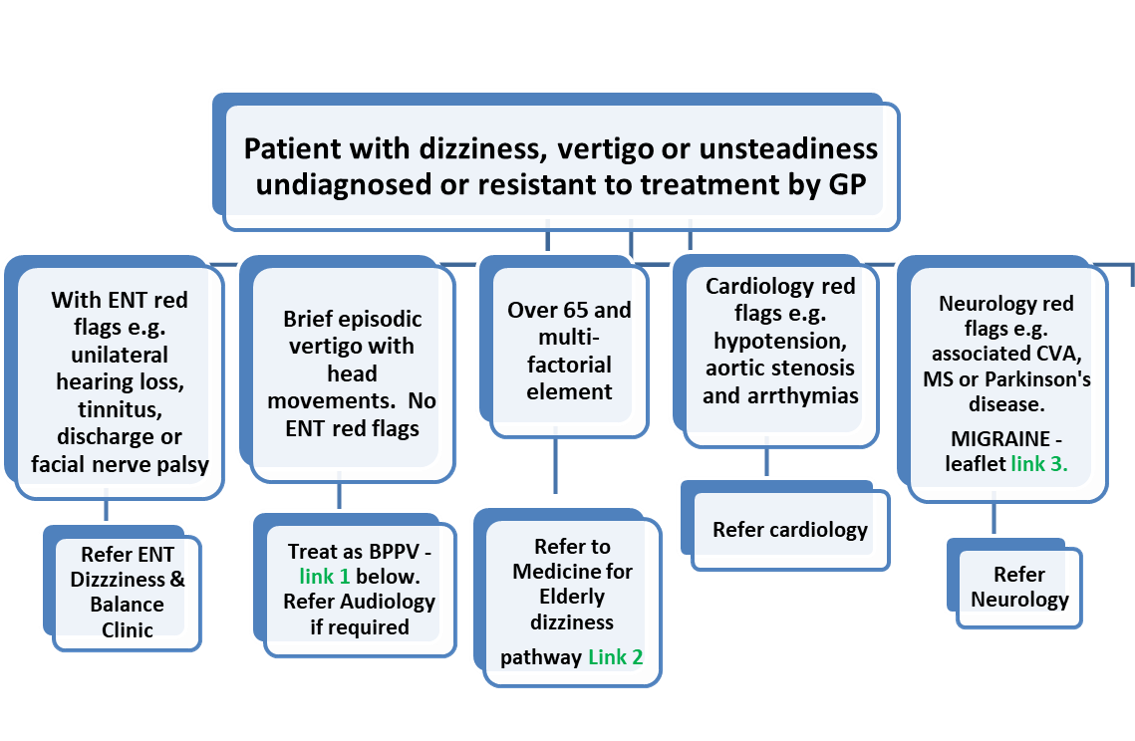
The history is key, with four main groups of patients:
- Peripheral vertigo – BPPV by far the commonest (see here)
- Vestibular migraine (and less commonly other neurological conditions)
- Balance issues in the elderly (multifactorial – see here)
- Cardiovascular causes.
The ENT balance team will ask patients to complete a symptom questionnaire online prior to being given an appointment, with the option of a phone call for those who cannot manage this.
Link 1- BPPVBenignParoxysmalPositionalVertigo.aspx
Link 2- Dizziness.aspx
Link 3- Advice for management of migraine in primary care (nhslothian.scot)
Please see the Primary Care Management page for more detail.
Who to refer:
- > 6weeks dizziness and balance problems for diagnosis and management:
- Probable Meniere’s – see Menieres disease.
Who not to refer:
Those with vestibular migraine:
- Standard Primary Care treatments are outlined management of migraine
- Please refer to Neurology for those not responding to first line treatments
- People over 65, particularly with co-morbidities, where the indications are that this is multifactorial – please see Dizziness
- Those with syncopal or pre-syncopal symptoms – please refer to Cardiology if suspicion of cardiac disease or arrythmias.
How to refer:
To ENT via SCI Gateway (specific SCI Gateway referral pathway under development).
The history establishes if vertigo is:
- truly rotational (rather than light-headedness or unsteadiness)
- CENTRAL or PERIPHERAL – distinguishing may be helped by the HiNTS test (please see here for Primary Care approaches and here for a demonstration).
If CENTRAL, consider the possibility of an acute cerebral event.
Prochlorperazine may be useful short-term, but prolonged use is not recommended.
Symptoms can be considered in four main symptom clusters:
- VERTIGO – peripheral causes:
- Intermittent brief episodes, precipitated by head movement or other postural changes are likely to be BPPV – see Audiology for details
- Acute onset with persistent symptoms:
- Vestibular neuritis (no hearing loss) or
- Labyrinthitis (often following infection and associated with unilateral hearing loss).
- Meniere’s disease is rare and associated with prolonged incapacitating episodes of vertigo, as well as hearing loss and tinnitus – please see here for more detail. There is commonly an element of BPPV when there is a mixture of symptoms – always worth treating that first.
- MIGRAINE and other neurological causes
MIGRAINE can cause true rotatory vertigo associated with light sensitivity +/- headache, occurring with menstrual cycle or more frequently, a past history of migraine.
Vestibular Migraine (previously known as migraine-associated vertigo) – please see guidance here for initial management, before any referral to the multidisciplinary balance clinic.
Vertigo may be associated with other central neurological conditions, including multiple sclerosis, cardiovascular events and Parkinson’s Disease.
- OLDER PEOPLE especially in the presence of co-morbidities.
Balance disturbance is often central or multifactorial – please see the Medicine of the Elderly pathway here for further detail. The team will see patients with vertigo where that is part of a more complex picture. Some may benefit from referral to the falls pathway.
- CARDIOVASCULAR CAUSES
- Tend to cause dizziness without vertigo – syncopal or pre-syncopal symptoms
- Often precipitated by standing up
- Causes include postural hypotension, cardiac arrythmias or severe aortic stenosis
- Please see here for further detail.













