Please see NHS Lothian Steroid Safety Bundle (PDF)
long-term-steroid-use-patient-Information-leaflet – appendix 1
Information
This guideline is aimed at all clinical health care professionals and nursing staff in NHS Lothian. It is designed to provide safe, practical guidance in the screening, diagnosis and management of complications related to long term high dose steroid therapy initiated in primary or secondary care.
Abbreviations: PPI = proton pump inhibitor, BGM = blood glucose monitoring, CGM = continuous blood glucose monitoring (such as dexcom or libre devices), BG = blood glucose, SU = sulphonylurea.
LONG TERM HIGH DOSE STEROID THERAPY = ≥ 10mg prednisolone (or equivalent) for > 14 days
| Prednisolone 10mg approx equivalent to |
|---|
| Hydrocortisone 40mg |
| Dexamethasone 2mg |
| Methylprednisolone 8mg |
| Betamethasone 2mg |
THINGS TO DO AT COMMENCEMENT OF LONG TERM STEROID THERAPY
- PERFORM an HbA1c and warn patient of symptoms of hyperglycaemia
- Hyperglycaemia is a potentially severe side effect of long-term steroid therapy particularly in the elderly and those with pre-existing diabetes.
- See screening and treatment guidance pages 2-3. Give patient information sheet appendix 1
- GIVE ADVICE ON ‘SICK DAY RULES’ and give STEROID EMERGENCY CARD (see patient information letter) – For advice on how to safely withdraw long term steroids see page 5
- GASTROPROTECTION: PPI (proton pump inhibitor) therapy should not be given routinely but should be considered for people at high risk of gastrointestinal bleeding or dyspepsia. (e.g. previous GI bleed, known GORD/peptic ulcer disease, currently on anticoagulation or active cancer).
- Bone Protection: Oral bisphosphates should be considered to prevent vertebral fractures in men and women on prednisolone doses of 7.5 mg daily or greater (or equivalent) for three months or more (total annual 630mg or more) where the BMD T-score at any site is less than -1.5. Treatment can be commenced while awaiting the results of DEXA. Please refer to Osteoporosis – RefHelp (nhslothian.scot) for more details and for those with intolerance to oral bisphosphonates or where oral bisphosphonates are contraindicated.
STEROID WITHDRAWAL ADVICE
Patients who have received long-term steroids in whom it is planned to reduce the dose below 4mg/day prednisolone (or equivalent) can be risk stratified for adrenal insufficiency by measuring a morning cortisol sample (brown tube) taken PRIOR to morning steroid dose. If it is safe to stop steroid treatment, an ongoing wean may still be clinically indicated.
| RISK | MORNING CORTISOL (nmol/l) | ACTION |
| HIGH RISK | <275 | Continue 4mg prednisolone and refer to endocrinology services. (If already in secondary care, perform short synacthen test pre morning steroid dose if possible) |
| MODERATE RISK | 275 – 425 | Can stop prednisolone Sick day dosing of 10mg prednisolone (or seek medical attention if unable to take) as per steroid emergency card for 3 months. |
| LOW RISK | >425 | Can stop prednisolone (if clinically indicated) |
STEROID ‘SICK DAY RULES’ AND SAFE STEROID WITHDRAWAL
Patients prescribed steroids at >5mg/day prednisolone (or equivalent) for over 4 weeks are at risk of adrenal suppression and therefore may be at risk of adrenal crisis.
| Steroid | Dose Equivalent |
| Prednisolone | 5mg per day or more |
| Methylprednisolone | 4mg per day or more |
| Hydrocortisone | 15mg per day or more |
| Dexamethasone | 500 microgram per day or more |
Patients at risk of adrenal crisis should be issued a STEROID EMERGENCY CARD (found in patient information leaflet appendix 1 and can be found at www.endocrinology.org/adrenal-crisis)
Sick day rule dosing for patients at risk of adrenal crisis is as follows (N.B. – if taking prednisolone 10mg daily or more, this is sufficient for rule 1 ‘moderate intercurrent illness’ cover and double dose not required)
Sick day rules
| Patient taking | <10mg prednisolone (or equivalent) | 10mg prednisolone or more (or equivalent) |
| Fever, infection needing antibiotics, surgery under local anaesthetic | Increase dose to 10mg prednisolone (or equivalent) whilst unwell or on day of procedure | Continue usual glucocorticoid dose |
| Persistent vomiting, preparation for colonoscopy, acute trauma, surgery under anaesthetic | 100mg Hydrocortisone IM/IV at onset/presentation/start of procedure then 50mg hydrocortisone IV QDS. Patient should be admitted for ongoing parenteral hydrocortisone if required. | 100mg Hydrocortisone IM/IV at onset/presentation/start of procedure then 50mg hydrocortisone IV QDS. Patient should be admitted for ongoing parenteral hydrocortisone if required. |
| Patients with confirmed adrenal insufficiency lasting >3 months should be seen in endocrine clinic for education about sick day rules and emergency hydrocortisone injection | ||
(https://www.rcpjournals.org/content/clinmedicine/20/4/371)
For perioperative and obstetric management please discuss with the anaesthetic team and consult national guidance (Management of glucocorticoids during the peri-operative period for patients with adrenal insufficiency | Association of Anaesthetists – www.anaesthetists.org).
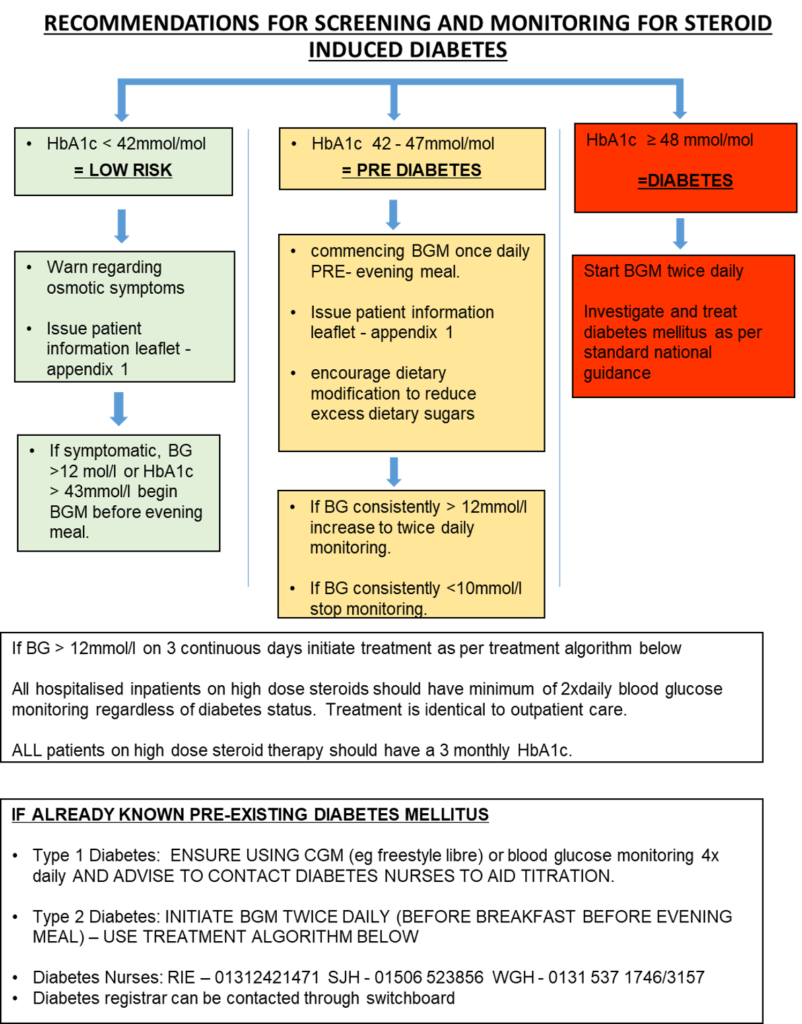
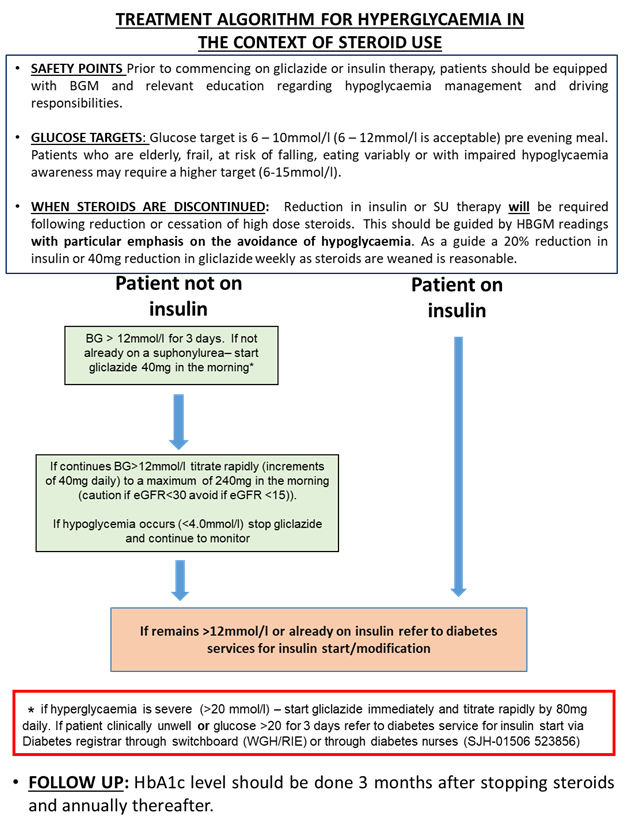
For Treatment of Hyperglycaemia in the context of steroid use, please see the primary care management section.
M.A & M.L 25-09-23
Long-term-steroid-use-patient-Information-leaflet.pdf
Society for Endocrinology free steroid emergency card and guidance Adrenal crisis | Society for Endocrinology
For perioperative and obstetric management please discuss with the anaesthetic team and consult national guidance (Management of glucocorticoids during the peri-operative period for patients with adrenal insufficiency | Association of Anaesthetists – www.anaesthetists.org).













