Lyme disease is an infection caused primarily by the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi which is transmitted to humans via tick bite. Those with outdoor occupations may be at higher epidemiological risk of infection.
The disease course can follow three stages:
Stage 1: Early, localised infection (3-30 days after tick bite):
- Erythema chronicum migrans (ECM)
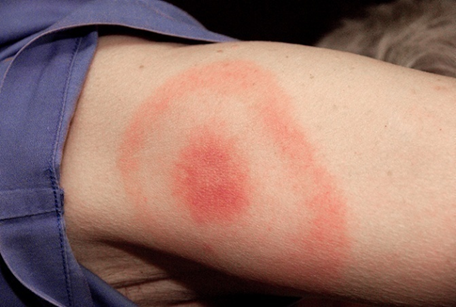
The characteristic ‘bullseye’ targetoid appearance is only seen in a minority of cases and the most common skin lesion is a homogenous, expanding rash > 5cm without central clearing. Serological confirmation of early Lyme disease presenting with ECM is not required, and may be negative in early infection. Patients with a single ECM lesion and no focal symptoms can be treated with oral antibiotics and managed in primary care.
Stage 2: Early disseminated disease (weeks to months following exposure):
- Constitutional flu-like symptoms, secondary erythema migrans or other rash
- Neuroborreliosis (includes cranial nerve palsies, radiculoneuropathy, mononeuritis multiplex, lymphocytic meningitis and rarely encephalomyelitis)
- Carditis (atrioventricular heart block, perimyocarditis)
- Arthritis (recurrent mono/oligoarthritis typically involving the knee – rare in Europe).
Stage 3: Late persistent disease (months to years following exposure):
- Late neurological complications (mainly peripheral neuropathy and encephalomyelitis)
- Chronic arthritis (rare in Europe)
- Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans (chronic bluish-red skin lesions on extensor surfaces)
- Ocular manifestations (including uveitis and iritis)
Please see Primary Care Management for full details about testing and treatment.
C.M & N.B 19-12-23
Who to refer:
Patients with confirmed (or high suspicion of) early disseminated or late manifestations of Lyme disease can be referred to Infectious Diseases unless specialty input is more appropriate.
Who not to refer:
Early, localised Lyme disease can be managed in the community. Advice is available via SCI Gateway.
Patients should not be referred to request unconventional treatments not currently recommended in the NHS (such as prolonged antimicrobial therapy) or to discuss the results of unconventional or non UK accredited tests carried out in the private sector or abroad. If there is a clinical suspicion of Lyme disease, please send repeat serology to the Scottish reference laboratory and use that result to guide management.
How to refer:
To Infectious Diseases at the WGH via SCI Gateway (including for advice)
Testing:
Scottish guidance on testing for Lyme disease and tick-borne infection is available from the Scottish Lyme Disease and Tick-Borne Infections Reference Laboratory.
Serology:
- 5mL brown cap gel tube or white cap tube for patients with symptoms of Lyme disease (excluding ECM) following tick exposure (GPOC/ICE via search button or by handwritten form).
- Antibodies are not detectable before 3 weeks post exposure and may take up to 10 weeks to develop.
- A negative early result does not exclude the possibility of B. burgdorferi infection.
- Repeat testing should be considered where there is a high index of suspicion for Lyme borreliosis.
Serology post treatment is not indicated and cannot be used to assess treatment success.
Treatment:
Early, localised Lyme disease can be managed in the community. Guidance on diagnosis and management is available from the NICE CKS Lyme disease summary.
Patients with a tick bite and ECM should be treated empirically. Testing is not indicated unless there is doubt about the diagnosis.
Summary:
| Scenario | Serology Indicated | Specialist Referral | Antimicrobials |
| Tick bite, asymptomatic | No | No | No |
| Tick bite, erythema chronicum migrans | No | No | Yes |
| Epidemiologic risk but non-specific symptoms or atypical rash | Yes (at least 8 weeks since exposure) | No | Yes if seropositive |
| Tick bite, specific complications e.g. ocular, cardiac, neurological, joint, or Paediatric case | Yes | Yes | Specialist advice |













