Introduction (from EPOS 2012-see Key guidance)
Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012
Images and text: European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012
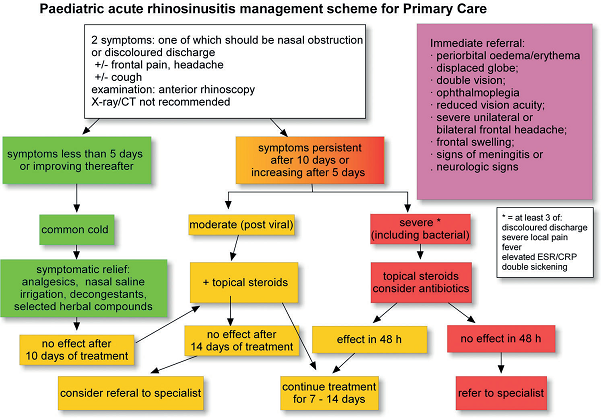
Acute rhinosinusitis (ARS) in children
Acute rhinosinusitis in children is defined as sudden onset of two or more of the symptoms:
- nasal blockage/obstruction/congestion
- or discoloured nasal discharge
- or cough (daytime and night-time)
for < 12 weeks;
with symptom free intervals if the problem is recurrent; with validation by telephone or interview.
Questions on allergic symptoms (i.e. sneezing, watery rhinorrhea, nasal itching, and itchy watery eyes) should be included. ARS can occur once or more than once in a defined time period. This is usually expressed as episodes/year but there must be complete resolution of symptoms between episodes for it to constitute genuine recurrent ARS.
Common cold/ acute viral rhinosinusits is defined as: duration of symptoms for less than 10 days.
Acute post-viral rhinosinusitis is defined as: increase of symptoms after 5 days or persistent symptoms after 10 days with less than 12 weeks duration.
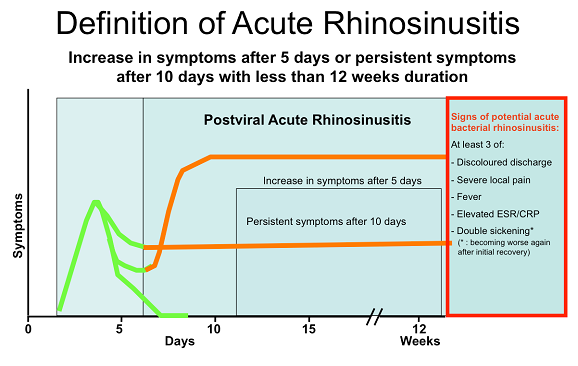
Acute bacterial rhinosinusitis (ABRS)
Acute bacterial rhinosinusitis is suggested by the presence of at least 3 symptoms/signs of
- Discoloured discharge (with unilateral predominance) and purulent secretions in the nasal cavity
- Severe local pain (with unilateral predominance)
- Fever (>38ºC)
- Elevated ESR/CRP
- ‘Double sickening’ (i.e. a deterioration after an initial milder phase of illness).