Plain X-Rays
Most referrals for Plain x-rays should be made via SCI Gateway using the Radiology Plain X-ray protocols under the specific location where the x-ray is to take place. In certain practices where there has been appropriate training they are able to use the ICE Ordering system to order Plain X-rays.
(If ordering electronically is not possible, such as in the event of significant IT failure, please use the appropriate paper X-ray department form. These should be sent via internal mail and when advising patients to phone to arrange the x-ray, allow 48 hours for form to arrive.)
After referral all plain x-ray requests need to be scheduled in by the patient phoning the appropriate department using the guidance above.
TELEPHONE BOOKING SYSTEM FOR PRIMARY CARE ELECTRONIC PLAIN FILM REQUESTS
All plain x-ray requests need to be scheduled in by the patient phoning the appropriate department.
In Radiology, we remain extremely grateful to you for using electronic requesting and the phone booking system. This has significantly improved how we deal with the large number of requests we receive and has improved the efficiency of the X-ray departments.
Please follow the following guidance for requesting Plain X-rays:
- The electronic referral MUST be made before a patient phones for an appointment
- The referrer must select the correct priority (Routine or Urgent) on the electronic referral before it can be sent. The majority of referrals will be Routine, however in certain circumstances (see below) the Referral should be requested as Urgent.
- Please ask the patient/carer to wait ONE WORKING DAY after submission of a referral before phoning for an appointment. This is because all x-ray requests must be vetted in accordance with IRMER rules
- Patients MUST phone the department to arrange an appointment, they should NOT PRESENT themselves to x-ray departments as they used to be able to. This may need to be explained clearly to patients who previously last attended for x-rays when walk-in was the system.
- Patients may have to wait several days for an appointment or be asked to attend another site for an alternative appointment.
- Please remember that Children under 16 should attend either the Royal Hospital for Children and Young People or St John’s Hospital for Plain x-rays.
- Patients MUST phone within 30 days of the referral being made (unless a follow up film has been recommended beyond the standard 4 weeks. Please see the Specific Referral Guidance section below on Follow up CXRs in primary care for more information regarding the arrangements in such cases).
How to discuss with patients arranging a plain x-ray
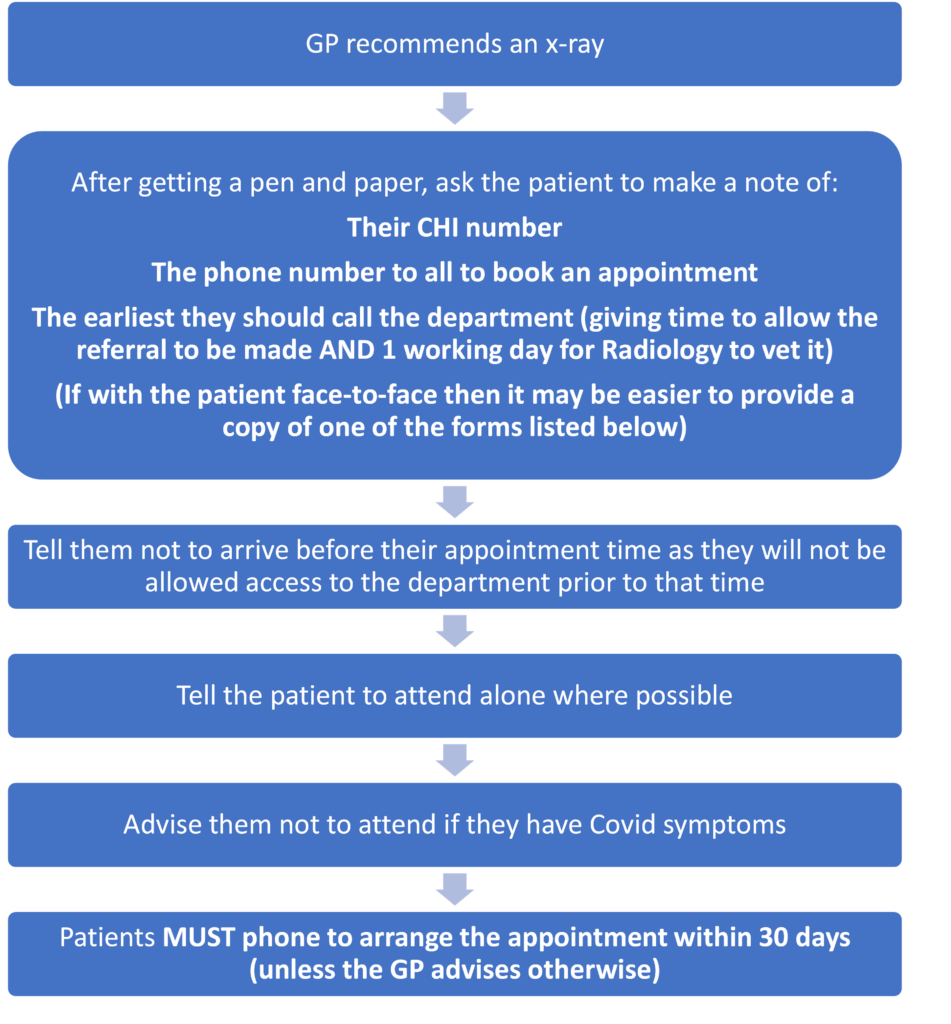
Where it is appropriate, the following forms may be helpful to GPs. They can be handed directly to the patient and lay out the current arrangements for x-rays in NHS Lothian. There are two versions of the form – the first one can be used with labels stuck on to provide patient details, the second version can be used by practices which use Vision as a Vision template.
Patient Information Sheet for X-rays – Label Form
Patient Information Sheet for X-rays – Vision Template
| Radiology Departments Contact Information for Patients to call Monday to Friday Only | |
| Leith Community Treatment Centre (8.30am-4.00pm) | 0131 536 6400 |
| East Lothian Community Hospital (8.30am-4.00pm) | 01620 642 732 |
| Midlothian Community Hospital (9.15am-4pm) | 0131 454 1045 |
| Lauriston Building (8.30am-4.00pm) | 0131 536 2942 |
| RHCYP (U16s only) (8.30am-4.00pm) | 0131 312 0880 |
| RIE (09.00am-5.00pm) | 0131 242 3700 |
| SJH (8.30am-5.00pm) | 01506 524 339 or 01506 524 350 |
| WGH (8.30am-5.00pm) | 0131 537 2054 |
Specific Referral Guidance
Please see the links at the top of this page for radiological guidance related to anatomical area, however the Radiology Department would like to highlight the specific pathways below. These are usually highlighted because they of either being high use pathways or because they have been recently amended:
Follow Up CXRs in Primary Care: In cases where a follow up film has been recommended beyond the standard 4 weeks this will be done and the patient will not be turned away. Please see below the diagram below for further information regarding the arrangements as well as the specific guidance outlined in the Edinburgh-Adult-Pneumonia-CXR-FOLLOW-UP-ADVICE-DEC-24.pdf
GP REQUEST FOR ? NOF#: If referring for assessment to rule out fractured NOF in patients who have had had a fall with hip pain and where A&E referral is not considered appropriate, please see the Radiology Flow Chart Radiology Guidance re GP REQUEST FOR NOF FRACTURE XRAY MARCH 2025 as to where the patient should be seen for x-ray. This is to avoid patients becoming stranded in community radiology clinics if they are found to need acute review.

Ultrasound
All referrals for Ultrasound should be made via SCI Gateway using the Radiology – Ultrasound referral form. For general ultrasound requests this referral pathway is available at:
- Leith Community Treatment Centre, East Lothian Community Hospital, Lauriston Building, Royal Infirmary Edinburgh, Western General Hospital, St John’s Hospital and Royal Hospital for Sick Children (only for children aged 0 to 16 NOT adults)
Patients will be sent appointments directly from Radiology, by letter or increasingly they may be sent their patient letters electronically. Patients may receive a text notification prompting them to log into a secure portal to view these letters.
Contacting Radiology
By Phone
PLEASE NOTE THESE NUMBERS ARE FOR PROFESSIONAL USE ONLY, THEY ARE NOT FOR PATIENTS
If GPs have any specific queries they can contact the Duty Radiologist for advice on the numbers below. (Patient department contact numbers can be found further up the page).
- WGH: GP contact number for Duty Radiologist 0131 537 2315
- SJH: GP contact number for Duty Radiologist 01506 524 352
- RIE: GP contact number for Duty Radiologist 0131 242 3572
- RHCYP: GP contact number for Duty Radiologist 0131 312 0120
By Email
The email addresses below can be used for administrative enquiries/ expediting reports/ changing appointments etc, but not for specific individual purely clinical questions. PLEASE NOTE THESE EMAIL CONTACTS ARE FOR PROFESSIONAL USE ONLY, THEY ARE NOT FOR PATIENTS
- WGH: wgh.radiology@nhs.scot
- WGH Mammography: wgh.mammography@nhs.scot
- RIE: radiology.rie@nhs.scot
- SJH: sjh.radiology@nhs.scot
If GPs have a query about a specific radiological report they can also email the reporting Radiologist directly.
UPDATED SG AND JB DEC 2025
Who to refer:
Please see individual pathways and the Primary Care Management section on Who to Refer
Referral for x-rays are governed by Ionising Radiation (Medical Exposure) Regulations 2018 and these are the responsibility of the Referrer.
For all Radiology requests: Referrers accept responsibility for dealing with the result(s) and informing the patient as necessary.
How to refer:
Plain x-rays: The majority of referrals for Plain x-rays should be made via SCI Gateway using the Radiology Plain X-ray protocols under the specific location where the x-ray is to take place. In certain practices where there has been appropriate training they are able to use the ICE Ordering system to order Plain X-rays
(If this is not possible, such as in the event of significant IT failure, please use the appropriate paper X-ray department form. These should be sent via internal mail and when advising patients to phone to arrange the x-ray, allow 48 hours for form to arrive.)
After referral all plain x-ray requests need to be scheduled in by the patient phoning the appropriate department using the guidance above.
Ultrasound: All referrals for Ultrasound should be made via SCI Gateway using the Radiology – Ultrasound referral form.
Guidance re Specific Plain x-ray and Ultrasound Investigations
Head and Neck – Skull
Who to refer (x-ray):
X-ray for palpable vault abnormality which feels bony
Who not to routinely refer for x-ray:
Headache – see guidance re CT Head, see also Neurology – Headache guidance
Headache suspicious of cancer – see guidance re Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers
Head Injury – if any concerns re intracranial injury, i.e. loss of consciousness, neurological defect, significant laceration, or haematoma – patient should be referred as an emergency to A&E
Note: Imaging departments may undertake skull X-ray as part of their imaging protocol for specific clinical problems e.g. skeletal survey for myeloma, but referral should specify the clinical indication for imaging.
Head and Neck – Face
Who to refer (x-ray):
X-ray for trauma to facial skeleton or mandible, not requiring attendance at A&E
X-ray for trauma to orbits including ?metallic foreign body, not requiring attendance at A&E
Who not to routinely refer for x-ray:
Middle or inner ear symptoms
Nasal trauma
Sinus disease
Temporal Mandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunction
Head and Neck – Neck soft tissues
Who not to routinely refer:
Suspected thyroid mass/goitre – refer directly to Endocrinology for all suspected thyroid disease. GPs should NOT refer for prior imaging.
Vascular/Carotid problems – refer to Stroke service for specialist assessment
Ultrasound for Salivary Glands
Chest
Who to refer (x-ray):
CXR Urgent Suspicion of Cancer (Remember to choose USC priority on the SCI GW Referral) as per SRGC and RefHelp Lung Cancer guidance
Any unexplained haemoptysis
Unexplained and persistent (more than 3 weeks): change in cough or new cough, breathlessness, chest/shoulder pain, loss of appetite, weight loss, chest signs, hoarseness, fatigue
Examination findings: focal chest signs, supraclavicular lymphadenopathy, New or not previously documented finger clubbing
Persistent or recurrent chest infection
Cervical and/or persistent supraclavicular lymphadenopathy
Thrombocytosis where symptoms and signs do not suggest other specific cancer
CXR Other indications:
Night sweats, fevers
Chronic respiratory conditions with unexplained change in symptoms
Unexplained increased CRP
Unexplained erythema nodosum
Strong suspicion of suspected underlying malignancy without obvious clinical primary (see additional RefHelp guidance here)
Post pneumonia follow up as advised by Radiology (Please see here for the Radiology Pneumonia Follow up protocol)
TB screening for new entrants to the UK from countries with a high prevalence of TB
Who not to routinely refer:
Chest trauma e.g. suspicion of rib fracture
COPD / Asthma follow up
Heart failure / hypertension without clinical change (Please see guidance on diagnosis of Heart failure where prior to referral a CXR is considered ‘Helpful but not essential’)
Infection / cough / wheeze in children
Pre-operative assessment
Routine follow-up in the absence of clinical deterioration (unless advised by radiologist)
Medical screening – unless employment related risk
Upper respiratory tract infection
Suspected costochondritis
CXR for patients requiring admission – Included here for info, these conditions require admission, and investigations will be arranged by Secondary Care
Acute respiratory distress
Suspected pulmonary embolus (rule out other pathology prior to CTPA)
Chest trauma – severe / penetrating injury
Acute severe chest pain
Suspected acute decompensated heart failure
Suspected pneumothorax
Suspected chest sepsis
Sepsis of unknown origin
Testes
Please see guidance on the Scrotal Conditions page for advice on when to refer for testicular ultrasound
Abdomen
Who to refer (ultrasound):
Palpable abdominal mass (indicate if mass is lower or upper abdomen as patient preparation may be different)
Jaundice
Suspected gallbladder disease
Suspected pancreatic disease
? Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Post cholecystectomy pain
? Hepatic metastases
Persistent unexplained abnormal LFTS – see RefHelp guidance on when to refer
Who not to routinely refer:
Constipation – (although AXR may be useful in frail elderly, psychiatric and patients with intellectual impairment)
Non-specific abdominal pain
Abdominal bloating
Dysphagia – See RefHelp Dysphagia guidance
Heartburn / hiatus hernia / dyspepsia –- See RefHelp Dyspepsia guidance
Intestinal blood loss – See RefHelp GI guidance
Suspected small bowel disease – See RefHelp GI guidance
Suspected colonic pathology – See RefHelp GI guidance
For abdominal wall masses see section on soft tissue/MSK Lumps and bumps
Suspected hernia should be referred to the Surgical Service without prior imaging
Renal Tract
Who to refer (ultrasound):
CKD
? Hydronephrosis
? Urinary retention not requiring admission
? Renovascular hypertension
? Renal mass
Recurrent UTI as per RefHelp Urology Recurrent UTIs guidance
Nonvisible haematuria as per RefHelp Urology NVH guidance
Trauma and haematuria not requiring admission
Loin pain where renal calculi not suspected
Loin pain in women <40 years
Who to refer (CT KUB):
Acute renal colic not requiring admission
Who not to refer:
Visible haematuria – see RefHelp Urology Visible Haematuria guidance
Plain film KUB – except for long term follow up of at-risk patients – spinal injury/previous lithotripsy
?Prostatic malignancy – for specialist referral
Gynaecology
Who to refer (ultrasound):
Palpable pelvic mass
Post Menopausal Bleeding in those not taking HRT: Please see RefHelp guidance on the Post Menopausal Bleeding (No HRT) page and make sure when referring for ultrasound to use the appropriate referral protocol on SCI Gateway
Unscheduled Bleeding in those taking HRT: Please see RefHelp guidance on the Unscheduled Bleeding on HRT – RefHelp and make sure when referring for ultrasound to use the appropriate referral protocol on SCI Gateway
Irregular menstrual bleeding/ inter-menstrual bleeding (not mid-cycle ovulatory bleeding)
Menorrhagia as indicated by Gynae Flowchart
Cyclical pelvic pain
Lost IUCD
Who not to routinely refer:
? PCOS (not routinely required -see guidance on RefHelp PCOS page re diagnosis of PCOS)
Menorrhagia without additional features suggesting ultrasound is required, as per Gynae Flowchart
Incidental finding of endometrial thickening in absence of PMB
Simple ovarian cysts where follow up not advised by Gynae / Radiology flow chart
MSK: Overall
Who to refer (x-ray)
Bone pain – symptomatic area only
? Myeloma – skeletal survey
? New arthropathy – x-ray affected joint only + hands/feet (single view) if RA suspected. For suspected OA (diagnosis confirmation) ensure symptoms >6 weeks; no previous x-ray.
? Osteomalacia – for local pain
? Osteomyelitis + Nuclear medicine – particularly in early disease when X-ray may be negative
Painful prosthesis – X-ray will not exclude all causes, if concerns with or without x-ray changes then refer to Orthopaedics urgently
Palpable bony mass – particularly if new/enlarging/painful and/or concerns re Primary bone tumour – this should be requested urgently and guidance in Sarcoma pathway followed, specifically the pathway for Suspected Bone Tumours
? Stress fracture
Trauma ?fracture not requiring attendance at A&E
Who not to routinely refer:
Routine Arthropathy follow up
Nonspecific musculoskeletal pain
Metabolic bone disease – biochemical tests usually suffice
Soft tissue mass – imaging prior to referral not usually advised – see guidance in Sarcoma pathway followed, specifically the pathway for Suspected Soft Tissue Tumours
MSK: Spine – Cervical spine
Who to refer (x-ray):
X-ray for ?Atlanto-axial subluxation (e.g. Down’s Syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis)
X-ray for ?Cervical Spondylosis with nerve root signs (MR preferred but not currently available as direct access)
X-ray for Injury with pain if not requiring admission
Who not to routinely refer:
Acute torticollis
? Cervical Spondylosis in absence of nerve root signs
Degenerative change
Dizziness / headaches
Whiplash injury without clinical findings
X-ray for injury with neurological deficit – these patients need A&E referral
MSK: Spine – Dorsal Spine
Who to refer (x-ray):
Injury with pain if not requiring admission
? infection
? Myeloma – ask for skeletal survey
? Osteoporotic vertebral collapse
? Primary malignancy – localised bone pain (Nuclear medicine may also be required)
Who not to routinely refer:
Acute back pain with no history of trauma (unless vertebral collapse suspected)
Degenerative change
? Metastatic bone disease (Nuclear medicine more sensitive)
Osteoporosis (unless vertebral collapse suspected)
Injury with neurological defect– these patients need A&E referral
MSK: Spine – Lumbar Spine
Who to refer (x-ray):
? Ankylosing spondylitis
? Spondylolisthesis
First onset back pain in older patients (>55 years) and younger patients (<20)
Injury with pain if not requiring admission
? Myeloma – ask for skeletal survey
? Osteoporotic vertebral collapse
? Primary malignancy – localised bone pain (Nuclear medicine may also be required)
Who not to routinely refer:
Acute back pain in adults – symptoms may settle, six-week rule – thereafter referral to the NHS Lothian integrated back pain service is advised NHS Lothian Integrated Back Pain Pathway
Chronic back pain in adults with no pointers to infection or neoplasm
? Osteoporosis (vertebral collapse
Back pain with red flag signs – Plain films can be misleadingly normal and arranging them can therefore delay appropriate investigation with CT / MRI. Secondary care referral as per the linked guidance should be arranged.
Injury with neurological defect– these patients need A&E referral
MSK: Spine – Whole Spine
Who to refer (x-ray):
Curvature of spine ?scoliosis or ?kyphosis (age 16-40)
Who not to routinely refer:
See reasons listed under individual guidance for cervical, dorsal, and lumbar spine
Patients younger than 16 and older than 40
MSK: Shoulder
Who to refer (x-ray):
? Rotator cuff calcification
Shoulder pain > 3 months
Trauma / dislocation – not requiring attendance at A&E
Who not to routinely refer:
? Impingement – specialist request
? Instability– referral to the Shoulder Physiotherapy Service is advised
? Rotator cuff injury – x-ray unhelpful for most rotator cuff problems – referral to the Shoulder Physiotherapy Service may be indicated
Shoulder pain – referral to the Shoulder Physiotherapy Service may be indicated
Shoulder ultrasound can’t be ordered directly by GPs in NHS Lothian, but may be requested by the Shoulder Physiotherapy Service if indicated
MSK: Pelvis and Hips
Who to refer (x-ray):
SI Joint problems
Trauma with inability to weight bear or persisting pain – not requiring attendance at A&E – if any risk of missed #NOF, please follow Radiology guidance re location of x-ray request
Suspected malignancy and hip pain
Clinical diagnosis of OA and no previous X-Ray
Unexplained undiagnosed hip pain >6 weeks and no previous X-Ray
? Avascular necrosis of the femoral head – if suspected then should refer for urgent Pelvic x-ray AND to Orthopaedics urgently as per guidance
Who not to routinely refer:
Hip pain – unless symptoms persist >6 weeks, risk of avascular necrosis or surgery considered
Trauma to coccyx
MSK: Knee
Who to refer (x-ray):
Knee pain with locking, restricted movement, or effusion
Knee pain when surgery considered
Trauma with physical signs – not requiring attendance at A&E
Suspected malignancy in patient with knee pain
Clinical diagnosis of OA and no previous X-Ray (symptoms >6 weeks and patient willing to undergo surgery)
Who not to routinely refer:
Knee pain without locking or restricted movement
? Osgood Schlatter’s disease
Trauma when physical signs are minimal
? Baker’s cyst – neither is ultrasound referral indicated to confirm the diagnosis
MSK: Ankle and Foot
Who to refer (x-ray):
Most general indications for bone and joint imaging apply (see Overall section above)
Who not to routinely refer:
Hallux valgus – except for pre-operative assessment
X-Ray for ? plantar fasciitis ? calcaneal spur
Trauma without: localised bony tenderness/ inability to weight bear/ significant soft tissue swelling
? Morton’s neuroma – refer to Foot/Ankle Service in the first instance
? Plantar fasciitis – refer to Foot/Ankle Service in the first instance
Discrete palpable mass ? ganglion/fibromatosis – refer to Foot/Ankle Service in the first instance
*Foot / Ankle ultrasound can’t be ordered directly by GPs in NHS Lothian, but may be requested by the Foot/Ankle Service if indicated*
Lumps and Bumps
Who not to routinely refer:
Lumps & Bumps should, in general, be referred to GP led Minor surgery or to General Surgery.
Suspected soft tissue cancer should be directed to the Orthopaedic Sarcoma clinic at RIE
Suspected hernia can be referred to the Surgical Service
Diffuse soft tissue swelling not suspicious of soft tissue cancer
Obviously, benign pathologies
Skin lumps and lesions
Clinical subcutaneous lipoma
Clinical sebaceous cyst
Mass <5cm diameter unless rapidly enlarging
Baker’s cysts: this is a clinical diagnosis. Referral is not indicated unless atypical and an alternative diagnosis is suspected
Breast lumps: All patients with suspected breast lumps, whether male or female, should be referred to the Breast Unit for assessment













