Distal interphalangeal joint (DIPJ) ganglion, commonly called a mucous cyst, or Dorsal digital ganglion cysts
Distal Interphalangeal joint ganglion commonly present as lumps on the dorsum of the finger at one or other side of the joint. They can also form at the edge of the proximal nail fold. They are harmless and will frequently resolve on their own.
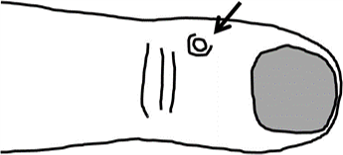
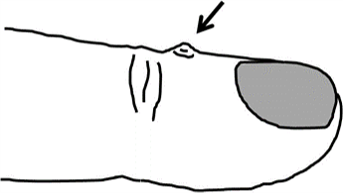
They tend to occur in older people and are usually associated with underlying joint degeneration (osteoarthritis of DIP joint).
- The lump can fluctuant in size.
- If they grow at the proximal nail fold, they can cause a nail deformity (groove or nail split) due to pressure on the germinal matrix.
- They can be painful, but it can be difficult to tell if the pain is coming from the lump or the underlying osteoarthritis.
- The mucous cysts can burst. The skin overlying can be thin and translucent. These factors can allow infection to develop and track deep into the joint.
- We do not recommend aspiration or bursting of mucous cysts, as this can lead to septic arthritis.
Surgical excision may be indicated for mucous cysts with thin skin or history of bursting, or those that cause a nail deformity.
Please see the patient information sheet (see primary care management tab) and print off and give to the patient.
It is usually best to leave the cyst alone unless it is causing significant symptoms. Any treatment of the cyst carries a risk that may leave the patient worse off.
Who to refer:
- Mucous cysts that have burst recurrently and are at risk of developing deep infection (septic arthritis)
- Mucous cysts causing significant symptoms in patient who have tried first line treatment options, and are willing to take the risks associated with surgery (see PRIMARY CARE MANAGEMENT SECTION)
- Please include a photograph of the patients lump
Who not to refer:
Patients who have not undergone first line treatment with minor or cosmetic symptoms (see PRIMARY CARE MANAGEMENT SECTION)
Direct referral to the hand service
Please include a photograph of the patient’s cyst/lump
Patient information leaflet – see separate document
Trial of first line treatment
We suggest at least a 3 month trial of first line treatment before considering referral for most mucous cysts
If the mucous cyst is small, not painful, and not affecting the movement of the finger, we recommend trying some simple, non-surgical treatments. Here are a few ways patients can manage it without surgery:
- Warm Compresses
Placing a warm, damp washcloth over the cyst for a few minutes a couple of times a day may help relieve any discomfort and keep the area flexible. - Finger Splinting
If your finger is sore, a splint can help keep it still and reduce pain. This is helpful if the cyst is inflamed (swollen and tender). You can buy a splint online for <£10 or use a lolly stick with tape to keep the finger still overnight. - Anti-inflammatory Gels
If the cyst is painful, you can use an anti-inflammatory gel, like ibuprofen or Voltarol gel, to help reduce swelling and pain. - Keeping the Area Clean
Since mucous cysts can occasionally pop on their own, it’s important to keep the area clean to avoid infection. If the cyst does open, cover it with a clean bandage
Never try to pop the cyst on purpose, as this can lead to infection or make the cyst worse.













