Information
These are guidelines for the diagnosis and management of suspected cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA) in primary care.
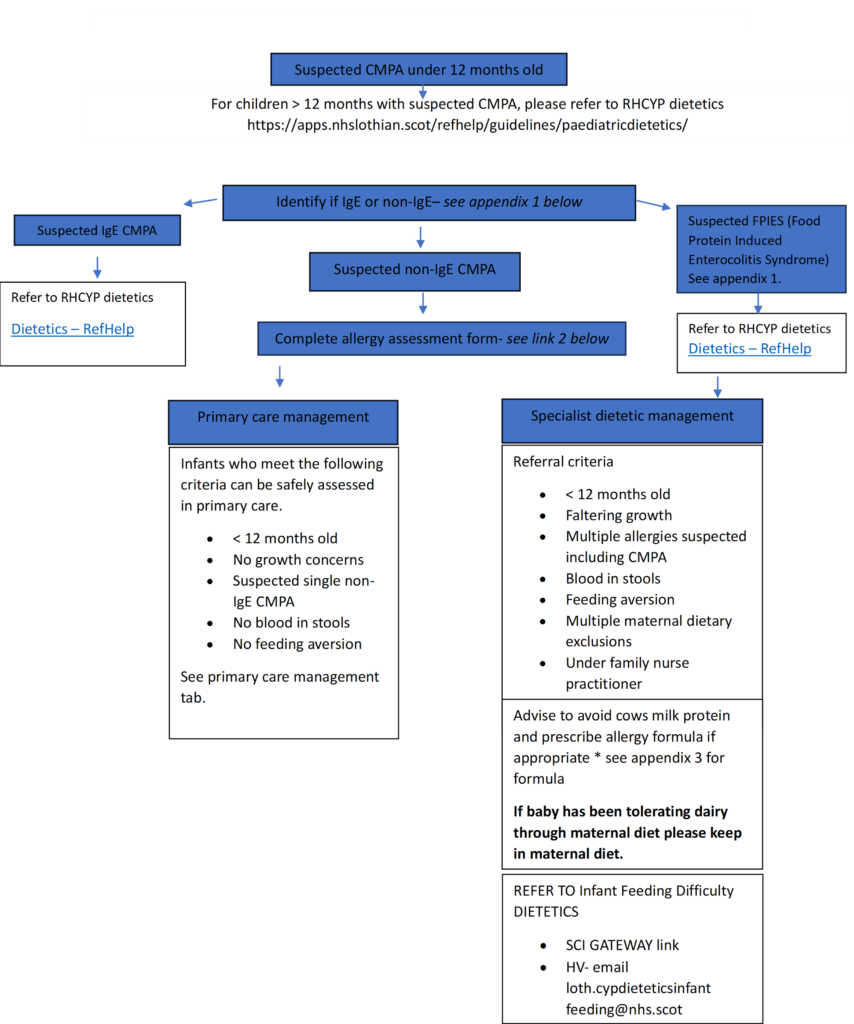
Please note there are no allergy tests for non-IgE mediated CMPA. Diagnosis is based on resolution of symptoms on a cows milk protein free diet AND reoccurrence on re-introduction of milk. Re-challenge is essential for diagnosis of non-IgE mediated CMPA. Do not re-challenge for suspected IgE mediated CMPA.
Introduction
- These guidelines are for the diagnosis and management of suspected cow’s milk protein allergy.
- The prevalence of cow’s milk allergy is up to 3% of infants during the first year of life.
- Cow’s milk protein allergy is frequently over diagnosed with allergy formula milks being over-prescribed.
- Cow’s milk protein allergy commonly presents in infancy, with most affected infants presenting with symptoms by 6 months of age.
- Cow’s milk protein allergy can be classified into IgE mediated reactions (immediate onset) and non- IgE mediated (delayed onset).
- Cow’s milk protein allergy will resolve in the majority of children during early childhood.
Dietetics – RefHelp (nhslothian.scot)
loth.cypdieteticsinfantfeeding@nhs.scot
Appendix-1-CMPA-signs-and-symptoms.pdf
Appendix-2-Infant-Allergy-Clinical-History-Assessment-Form-for Doctors and Health Visitors v1.doc
Appendix 3 PRESCRIBING-ALLERGY-FORMULA-MILKS.pdf
D.R.M & L.W 15-11-24
Who can refer:
GPs, Health Visitors, Paediatric Physicians, Family Nurse
Who to refer:
- Infants with suspected non-IgE CMPA who meet the criteria for specialist dietician management as per the above flow chart e.g:
- < 12 months old
- Faltering growth
- Multiple allergies suspected including CMPA
- Blood in stools
- Feeding aversion
- Multiple maternal dietary exclusions
- Under family nurse practitioner
- Infants with suspected non-IgE CMPA who meet criteria for initial primary care management but who develop further symptoms following a subsequent milk challenge.
Who not to refer:
- Infants with suspected IgE CMPA – Please refer these infants to RHCYP General Paediatric Dietetics. Do not re-challenge for suspected IgE mediated CMPA.
- Infants with suspected non-IgE CMPA who can be assessed safely in primary care and who do not develop symptoms following a subsequent milk challenge following a period off dairy. See Primary Care Management tab.
How to refer:
- A Sci-Gateway referral pathway is currently under development for this service. In the meantime please email loth.cypdieteticsinfantfeeding@nhs.scot with allergy assessment form attached.
After Referral:
Please see below detailing what families should expect from the Dietetic CMPA pathway following confirmation of CMPA diagnosis:
- Maternal dietary measures for breast fed infants, or allergy formula for formula fed infants, should continue whilst awaiting review (see Primary Care Management tab).
- Family will be called at 5 months of age and booked into cow’s milk free weaning group (in person or online). To continue dietary measures for breast fed infants or allergy formula for formula fed infants.
- Family will be called at 12 months of age and booked into cow’s milk reintroduction group (online)
- Discharged from dietetics after 12 months of age, unless ongoing dietetic review required. Prescription of allergy formula discontinued.
- One to one dietetic clinic appointments can be arranged as required where appropriate.
We have close working relationships with RHCYP Medical Paediatrics and Allergy teams and can forward referrals as appropriate
The following patients can be safely assessed and have initial management carried out in primary care:
- <12 months old
- No growth concerns
- Suspected single non-IgE allergy to milk
- No blood in stools
- No feeding aversion
Step 1:
To confirm/refute non-IgE CMPA diagnosis, complete 4 week dairy exclusion and subsequent milk challenge following guidance in the information sheets.
See parent information sheet for breast fed babies
See parent information sheet for combination fed babies and formula fed babies.
If baby was previously tolerating dairy through maternal diet and became symptomatic on introduction of formula milk please advise Mum to continue to keep dairy in her own diet.
For formula fed infants, please prescribe appropriate allergy formula
PLEASE NOTE: If no improvement after 2 weeks minimum on extensively hydrolysed formula, consider trial of amino acid formula for a further 2 weeks minimum, or alternative diagnosis eg. gastro-oesophageal reflux.
See parent information sheet for babies on solids
Step 2:
If CMPA confirmed on re-challenge, please refer to infant feeding dietetics – see the Referral Guideline tab – IFD mailbox –loth.cypdieteticsinfantfeeding@.nhs.scot (SCI-gateway protocol under development)
Please continue allergy formula milk
Please see “after referral” in the Referral Guidelines tab to inform family of what to expect from dietetics
If no return of symptoms on milk challenge, resume normal diet and consider alternate diagnosis.
Infant Allergy Assessment Form for Doctors and Health Visitors
Milk challenge information sheets
- Milk-free trial and re-challenge information for breastfed children with suspected non-IgE CMPA: https://policyonline.nhslothian.scot/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Milk-free-trial-and-re-challenge-information-for-breastfed-children-with-suspected-non-IgE-CMPA.pdf
- Milk-free trial and re-challenge information for formula fed children with suspected non-IgE CMPA: https://policyonline.nhslothian.scot/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Milk-free-trial-and-re-challenge-information-for-formula-fed-children-with-suspected-non-IgE-CMPA.pdf
- Milk-free trial and re-challenge information for breastfed children on solids: https://policyonline.nhslothian.scot/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Milk-free-trial-and-re-challenge-information-for-breastfed-children-on-solids.pdf
- Cow’s milk protein allergy – frequently asked questions. : https://policyonline.nhslothian.scot/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/CMPA-and-feeding-difficulties-FAQ.pdf
Feeding difficulties in babies- what is normal: https://policyonline.nhslothian.scot/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Feeding_difficulties_in_babies.pdf
Food allergy and eczema: https://policyonline.nhslothian.scot/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Food-allergy-and-eczema-FAQs.pdf
Dyschezia: https://policyonline.nhslothian.scot/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Dyschezia-in-babies.pdf
Feeding Difficulties in Infants Under 6 Months – RefHelp (nhslothian.scot)













