History
- Elderly/older patients
- Younger post traumatic/post operative
- Restricted activities of daily living
- Reduced walking
- Previous diagnosis/other OA joints
- Persistent pain
Signs
- Limp
- Decreased range of movement
- Deformity
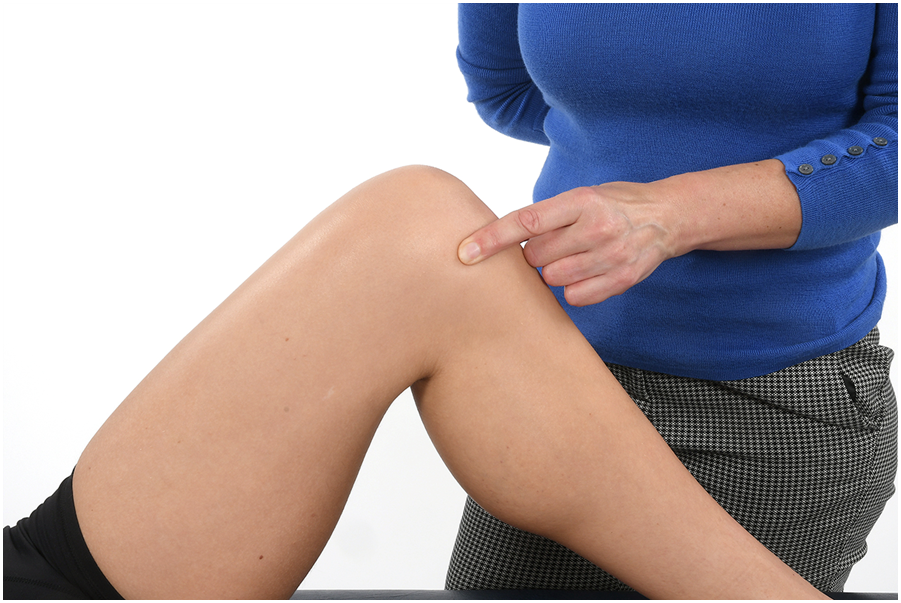
- Medial joint line pain. image copyright NHS Lothian
- Possible effusion
- Possible crepitus
- Stiffness after sitting/in the morning
- Unable to kneel or squat
- Possible old surgery scars
- Exclude hip joint as cause (groin pain, hip stiffness)
Medial joint line pain. image copyright NHS Lothian
Secondary care referral
- If X-Rays show established OA changes, all primary care treatments have been exhausted and patient wishes an opinion on surgical options, refer to Arthroplasty service
- If all primary care treatments have been exhausted, consider referral to Non Arthroplasty Knee Service
Primary care investigations
- X-Ray – AP standing & lateral
Primary care treatment
- Analgesia
- Physiotherapy
- Cardiovascular exercise
- Strengthening exercises
- Weight loss
- Walking aids
- Corticosteroid injection if swollen and no other contraindications to csi**
** corticosteroid injection not to be given within 6 months of knee replacement surgery due to increased risk of infection at time of surgery













