The 2017 American Thyroid Association (ATA) guidelines [9] advise that there is no strong evidence that treating maternal sub-clinical hypothyroidism improves neurocognitive outcomes in children, but there is some evidence that sub-clinical hypothyroidism is associated with increased risks of pregnancy loss or preterm delivery. There is also no evidence to support universal screening of women for thyroid disease. However, women with sub-clinical hypothyroidism who are planning pregnancy or become pregnant should be advised to seek GP review for a check of thyroid function and TPO antibodies and consideration of levothyroxine replacement depending on their results (see guidance and algorithm below). The following advice on the approach to subclinical hypothyroidism in pregnancy is based on the 2017 ATA guidelines. [9]
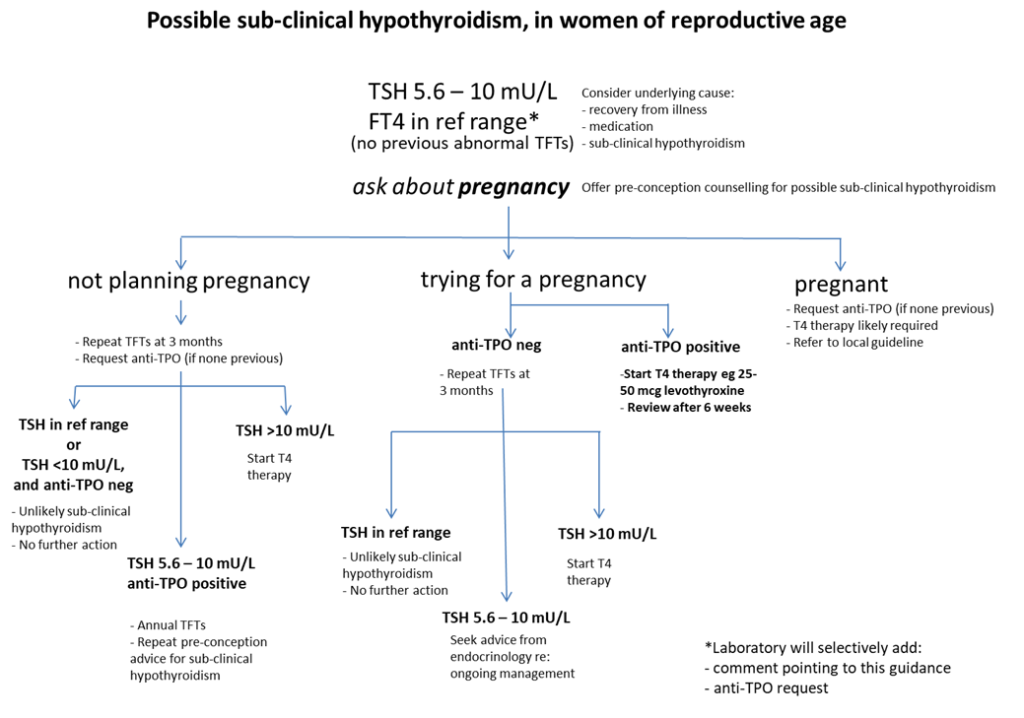
Management and treatment advice is summarised in the algorithm below:
- T4 therapy is recommended for TPO Ab-positive women with a TSH greater than the pregnancy-specific reference range and for TPO Ab-negative women with a TSH greater than 10.0 mU/L. A starting dose of 25-50mcg levothyroxine is recommended. If advice is needed, an ‘advice only’ request can be sent via SCI Gateway
- T4 therapy should be considered for TPO Ab-negative women with TSH concentrations greater than the pregnancy-specific reference range and below 10.0 mU/L, aiming to bring the TSH down to 2.5 mU/l or below. After pregnancy, levothyroxine could be withdrawn. A starting dose of 25-50mcg of levothyroxine is reasonable. If advice is required, cases can be discussed with a consultant endocrinologist by sending an ‘advice only’ referral on SCI Gateway.
- TPO Ab-positive women with TSH concentrations >2.5 mU/L and below the upper limit of the pregnancy-specific reference range: although the 2017 ATA guidance suggested that T4 therapy may be considered for these women, the more recent TABLET trial suggests that use of Levothyroxine in euthyroid women with positive anti-thyroid antibodies DOES NOT improve obstetric outcomes.[10] Therefore, we no longer recommend Levothyroxine therapy in this group.
- T4 therapy is not recommended for TPO Ab-negative women with a normal TSH (TSH within the pregnancy-specific reference range).
REFERENCES – please see the Resources and Links section of the main Thyroid Conditions and Pregnancy page.
C.M. & N.Z. 08-07-24













