Scabies is a contagious mite infestation characterised by:
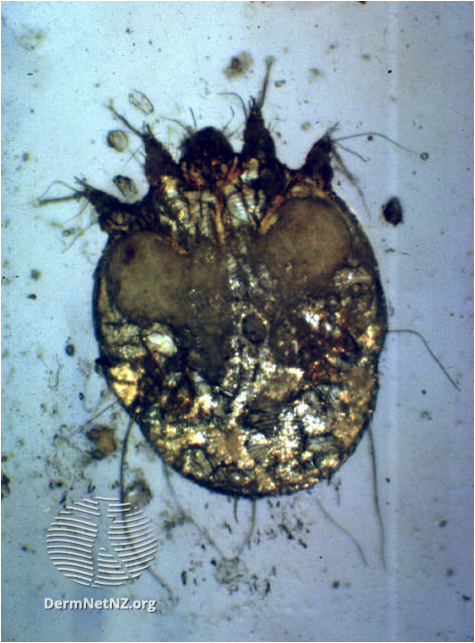
- An intense itch, especially at night, involving all body regions except the head (in adults).
- Pathognomic burrows (containing a mite at the leading end), typically on palms, fingers, wrists and insteps, and inflammatory nodules on penile and scrotal skin.
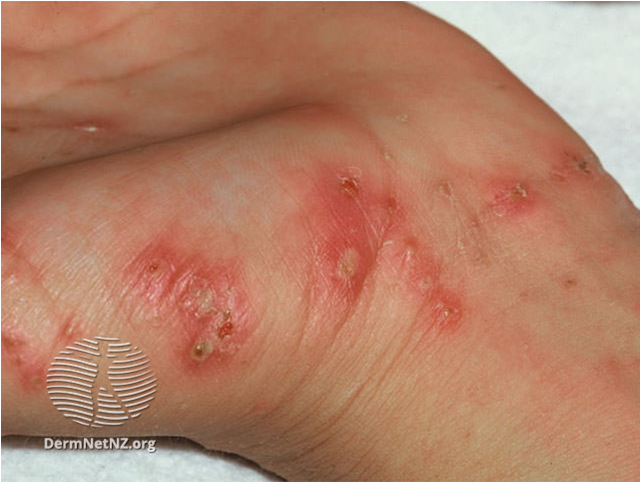
- A non-specific excoriated eruption (representing an allergic reaction to the infestation) involving trunk and limbs.
- Scalp involvement in infants and young children.
All images on this page are sourced from DermNet | Dermatology Resource (dermnetnz.org)
R.C 24-05-24
- Diagnostic uncertainty /failure to respond to appropriate treatment
- Patients under two months of age
- Crusted (Norwegian) scabies
Management
- Reassure patient that treatment is curative.
- Provide a patient information leaflet (British Association of Dermatologists).
- Two overnight (8-12 hours) applications of 5% permethrin cream, or 24 hour applications of 0.5% malathion lotion, should be used one week apart; the first cycle should eradicate all adult mites, and the second will deal with any developing mites that have hatched in the interim from eggs that have survived the first treatment cycle.
- Apply to all regions of skin from the chin downwards (the head should be treated in children under 2 years, the immunocompromised and the elderly), paying particular attention to sites of burrows and beneath the free edges of the nails.
- Reapply treatments to hands or nappy region if they are washed.
- To reduce the risk of re-infection, simultaneous treatment of all close contacts, including household members, whether symptomatic or not.
- Clothing, towels and bedding should be left in a plastic bag for a few days, and then put through a standard wash cycle.
Therapeutic Tips
- Warn patient that itching may persist for several weeks (and scabetic nodules several months) following successful treatment.
- Antipruritic measures, such as a moderately potent or potent topical corticosteroid, 1% or 2% menthol cream, crotamiton cream, calamine lotion or a nocturnal dose of sedating antihistamine, can help alleviate the itch.
- Young children should wear mittens during the treatment cycle to minimise ingestion of the acaricideInvolve public and environmental health if outbreak is in hospital, nursing or residential home, school, nursery or other group setting: consult local guidelines.
- Crusted scabies is highly infectious, and affected patients should be isolated.
- Treat secondary bacterial infection and exacerbation of pre-existing skin conditions, such as eczema and psoriasis.
- Avoid permethrin in patients allergic to chrysanthemums (as can cause allergic dermatitis).
- Permethrin 5% cream is flammable.
- Persistent symptoms usually mean inadequate treatment, re-infestation or, rarely, drug resistance.













