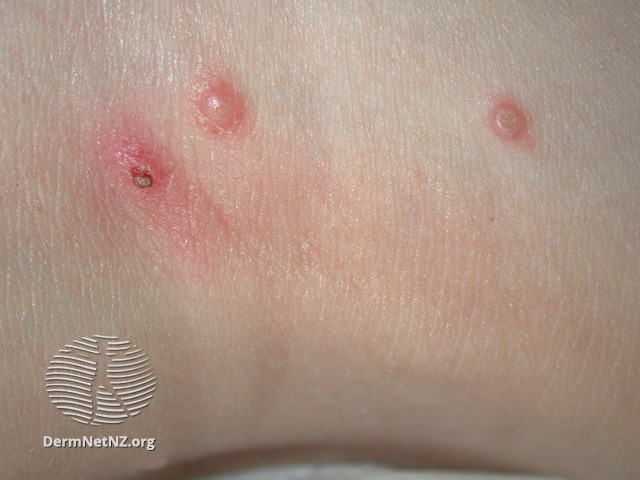
Molluscum Contagiosum is a common acquired infection of childhood due to a pox virus. Most infections resolve spontaneously within 6-18 months, though some can last longer. Longer duration is more common in patients with atopic eczema or immunosuppression.
Young adults may also develop molluscum contagiosum – sometimes due to sexual transmission. Widespread lesions can be found in those with HIV or immunosupression.
Lesions may become itchy if there is surrounding eczema or inflamed and crusted and this often heralds resolution.
R.C 24-05-24
Criteria for Referral
- Diagnostic uncertainty.
- Immunosuppressed patients with widespread persistent lesions (may present on the face/perioral skin)
Management
In the majority of cases no treatment is required as spontaneous resolution occurs and parents should be encouraged to allow this to happen.
Treatment can be painful and/or increase the chance of scarring and should be reserved for adults, older children and problematic lesions.
- Avoid sharing of towels and sponges to prevent spread
- Topical antiseptic may minimise secondary infection
- Topical potassium hydroxide 5% is licensed from the age of 2 years. It is available from pharmacies and should be applied to each spot twice daily until these become inflamed (or no more than 14 days).
- Cryotherapy may be used but is painful and an option of last resort (avoid in young children)
- Eczema around molluscum: treat with emollients or mild topical steroid or combination antibiotic and topical steroid cream.
- Consider topical salicylic acid gel for non-facial lesions (do not use on facial lesions).
- Provide a patient information leaflet – http://www.bad.org.uk/shared/get-file.ashx?id=220&itemtype=document
For Patients
For Health Professionals
- Primary Care Dermatology Society Molluscum-Contagiosum Guidance













