Hand and foot eczema is often multi-factorial. Causes include atopic eczema, irritant dermatitis or allergic contact dermatitis. It can be itchy and may be vesicular, bullous or hyperkeratotic. Fissures may be evident.
Pompholyx is a specific type of eczema that causes intensely itchy vesicles and/or blisters on the palms and sides of fingers and/or on the soles of the feet.
A good history helps to determine what the underlying cause may be.
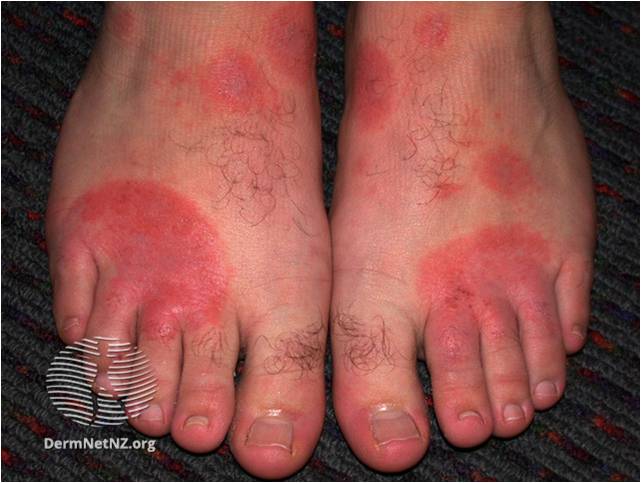 | 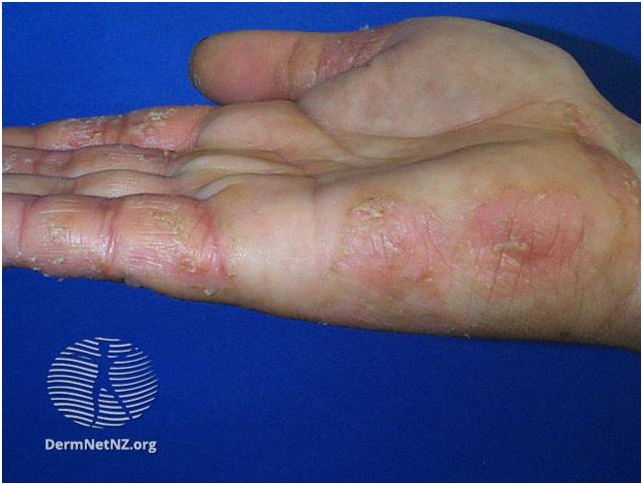 | 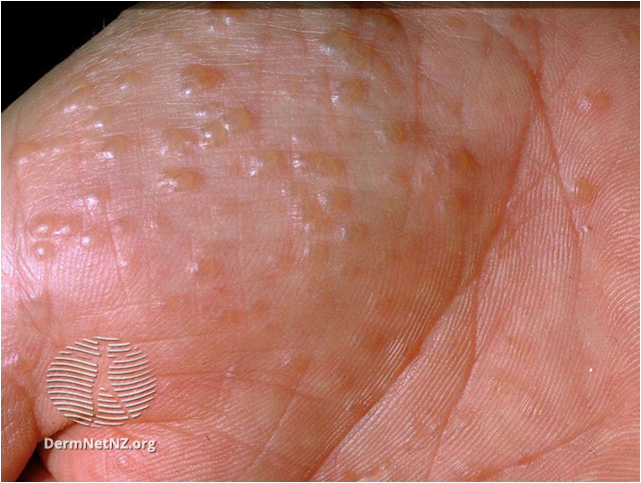 |
| Shoe contact dermatitis- Search DermNet | DermNet (dermnetnz.org) | Atopic hand dermatitis – Search DermNet | DermNet (dermnetnz.org) | Pomphylox – Search DermNet | DermNet (dermnetnz.org) |
R.C 24-04-24
Dermatology Referral Criteria
- Poor response to continuing potent or very potent topical steroids.
- Recurrent secondary infection.
- Clinical history of occupational exacerbations where there is likely to be frequent exposure to detergents, fragrances and chemicals.
- Suspicion of contact allergy, which may be occupational or hobby related (for consideration of patch testing).
- Impact on quality of life at work or at home.
Therapeutic Tips
- Attention to good hand care includes the use of protective gloves, and avoidance of irritants such as soap, shampoos and detergents.
- Patients should be encouraged to use a suitable emollient as often as possible and to have emollients both at home and work.
- Prescribe adequate quantities of emollients, soap substitutes (+/− antiseptics) Patients may need up to 500g emollient per week on a repeat prescription. Consider ointment based emollients (under cotton gloves if tolerated) in the evening. Remember to warn patients about potential fire hazard of emollients, especially if they smoke.
Management
- Consider underlying cause or predisposing factors including atopy / profession / hobbies.
- Consider differential diagnoses such as: psoriasis, fungal infection, palmar plantar pustulosis
- Assess, swab and treat any secondary bacterial infection.
- Mycology skin scraping for tinea, particularly if unilateral changes or one hand and both feet affected.
- Avoid irritants.
- Soap substitute – lotion, cream or ointment depending on patient preference.
- Apply emollients frequently throughout the day and recommend ointment emollient under cotton gloves at night.
- Potent / very potent topical steroids (step down potency or frequency of application for continued maintenance if required)
- If weeping/ severe blistering soak hands/ feet in 1:10,000 solution of potassium permanganate for 10 mins (potassium permanganate solution tablets 400mg 1 tablet dissolved in 4 litres of water). Warn patients nails may stain brown. Warn patients NOT TO DRINK the solution.
- Salicylic acid containing ointments can be useful in hyperkeratotic eczema.
- Fludroxycortide tape to fissures.
For Patients
http://www.bad.org.uk/shared/get-file.ashx?id=166&itemtype=document
http://www.bad.org.uk/shared/get-file.ashx?id=3776&itemtype=document
For Health Professionals
http://www.pcds.org.uk/clinical-guidance/eczema-hand-dermatitis
http://www.dermatology.nhs.scot/dermatology-pathways/pathways/eczema-hand-and-foot/













