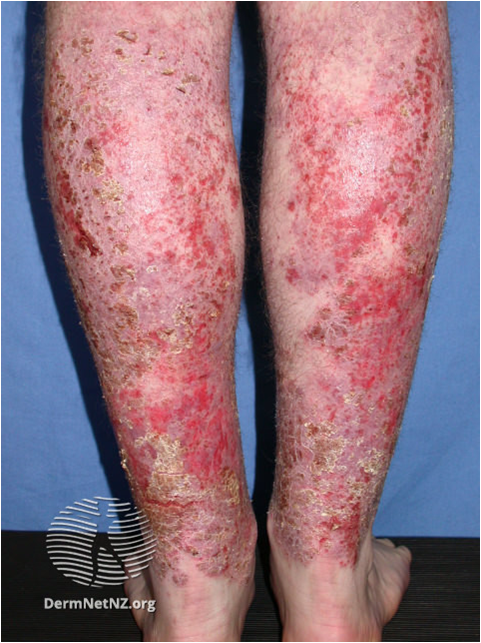
Atopic eczema is a common relapsing and remitting skin disease. While some individuals seem to ‘grow out’ of their eczema during childhood, or experience long periods of remission, a significant proportion of patients will have ongoing chronic disease in adulthood which can flare particularly at times of stress. Regular treatment is required.
In secondary care we offer phototherapy and a range of immunosuppressant drugs to manage moderate to severe disease, as well as investigations such as patch testing and photo testing. New targeted biologic drugs are also becoming available. While most patients can be managed in general dermatology clinics, the patients with the most severe disease will be managed in the dedicated adult eczema clinic.
R.C 24-05-24
Dermatology Referral Criteria
Routine or urgent general dermatology SCI Gateway referral depending on severity:
- Diagnostic doubt
- Failure to respond to continuing use of appropriate topical moderately potent treatment. Please see ‘suggested topical treatment regimes’ in the Primary Care Management tab for more information
- Sleep problems and psychosocial upset
- Recurrent secondary infection
- Persistent facial or flexural disease which may respond to a topical calcineurin inhibitor
- History suggestive of contact allergy
- Facial eczema, particularly peri-ocular eczema
- Hand eczema, particularly if affected by or affecting occupation
- Patient requesting oral steroids to manage their eczema. Oral steroids can cause a rebound flare when they are stopped and make atopic eczema more unstable and difficult to manage
Emergency referral (contact on-call dermatology registrar via NHS Lothian Switchboard)
- Suspected eczema herpeticum
- see Primary Care Management tab for more information
- Erythrodermic eczema (>90% coverage +/- systemically unwell)
There is a lack of high quality evidence for many of the strategies and interventions used to treat atopic eczema. Sometimes this is because of the difficulty in doing high quality trials in this area. The suggestions below are based on local practice in Lothian and which patients may find helpful to try. Further information is available via the links under the Resources tab.
Therapeutic tips
- Reassure patients that topical steroids are safe and effective. Ointments are preferable to creams as they contain fewer potential sensitisers.
- Irritants should be avoided i.e. soaps, fragrance, harsh washing powders.
- Dietary modification is usually not required.
- Avoid oral steroids if at all possible for eczema management. The short-term improvement is unlikely to be sustained and the eczema can become more unstable.
- A written action plan can help inform patients how to manage their eczema (see link in Resource tab).
General Management
SOAP SUBSTITUTES AND ANTISEPTICS
- Prescribe soap substitutes for washing with in shower/bath and for handwashing. Consider trying emollients with added antiseptics if recurrent skin infection is a problem
- While eczema severity correlates with carriage of S.aureus, there is no clear evidence that reducing bacterial carriage with antiseptics helps to reduce eczema severity. Treating eczema with topical steroids may reduce bacterial carriage by improving skin integrity.
- Although RCT evidence for their effectiveness in managing atopic eczema in children is lacking, some patients may find bath emollients helpful (and it will discourage the use of fragranced bubble baths)
- Although RCT evidence for their effectiveness is lacking, some patients find twice weekly bleach (Milton) baths helpful – see link to pdf in Resources Tab.
EMOLLIENTS and GARMENTS
- Encourage regular emollient application (minimum twice daily)
- prescribe sufficient quantities – approximately 500g per week – of patient’s preferred emollient(s). Lighter cream based emollients may be preferable during the day, and greasier ointment formulations may be beneficial at night. Give patients a range of products to try. Warn of flammability risk with greasy formulations. Patients should be advised to use a clean spoon or spatula to dispense emollients from tubs to reduce the risk of bacterial colonisation. Pump dispensers can be helpful in this regard.
- Lightweight plain-knitted elasticated cotton tubular bandages can keep treatments in place and avoid staining of clothing (i.e. Clinifast or Comfifast stockinette, prescribe appropriate width for affected limbs and patients can cut appropriate lengths)
- Light cotton clothing, or prescription garments may also be helpful and easier to use (ie Clinifast stockinette garments, Comfifast Easywrap garments, Skinnies Viscose stockinette garments, Dermasilk garments). Patients will need several sets.
ANTIHISTAMINES - Sedating antihistamines taken at night may be helpful for itch, by causing a deeper sleep. Non-sedating antihistamines are not likely to be effective in supressing the itch of eczema as it is not thought to be histamine driven.
TOPICAL STEROIDS
Topical steroids should generally be used once daily. If there is a lack of response, twice daily application can be tried.
Many patients can be too sparing in their use of topical steroids. Check the finger tip unit (FTU) guide or calculate appropriate steroid use in grams per week according to sites of application (links below) and prescribe sufficient quantities.
1 FTU= enough steroid cream/ointment to cover centre of distal phalanx of index finger. This is sufficient to then cover skin the size of the area of both palms of that person. See Resources tab.
| Suggested topical steroid regimes by body site using LJF products | |
| Face/neck | 0.5% or 1% hydrocortisone ointment once daily for 5-7 days. If response not satisfactory, try twice daily application for 5-7 days. Occasionally severe facial eczema may need a moderate potency steroid e.g. clobetasone butyrate 0.5% ointment. This should be used for short periods only i.e. 3-5 days, and then stepped down to hydrocortisone for 5-7 days. |
| Trunk/limbs | Moderate potency topical steroid e.g. clobetasone butyrate 0.5% ointment once daily for up to 14 days. If no response, or if eczema is particularly severe at the outset, use a potent topical steroid such as betamethasone valerate 0.1% ointment for up to 14 days. |
| Hands/feet | These often need potent topical steroids to have any effect. Try a potent topical steroid such as betamethasone valerate 0.1% ointment for up to 14 days. If no effect, and you are confident of the diagnosis, consider trying a super-potent topical steroid such as Clobetasol propionate 0.05% for up to 7 days. |
| Flexures | Particular care needs to be taken in the flexures (i.e. axillae, groins/genital area) as the risk of cutaneous atrophy is higher with frequent use of topical steroids. Use mild or moderate potency topical steroids only, and for short courses (5-7 days of daily use). |
| Eczema responds? | Patients should be encouraged to slowly reduce frequency of topical steroid application over approximately 2-3 weeks (all sites) |
| No response to initial treatment? | Consider infection. If signs of clinical infection, oral antibiotics (in conjunction with topical steroid use) will often help stubborn disease. Flucloxacillin is a good first choice, with clarithromycin for penicillin allergic patientsIs the patient using enough topical treatment? Check a finger tip unit guide for topical steroids and encourage copious emollient use – aim for at least 500g per week of emollient in widespread diseaseEczema on the trunk/limbs/hands/feet may benefit from occlusion with light cotton tubular bandages, garments and/or gloves over topical treatments. This will increase the absorption of the topical preparations (so caution with potent or super-potent topical steroid use on widespread areas).Consider offering a soothing anti-inflammatory preparation such as 1% ichthammol in YSP (made by Tayside Pharmaceuticals) which can be applied as a paste on the trunk/limbs/hands/feet under bandaging, garments or gloves |
| Recurrent flares? (more than 4 per year) | Try a maintenance approach for patients with moderate to severe eczema – patients apply the topical steroid that they would use for a flare on 2 consecutive days per week (e.g. weekends) for several months to see if this helps with disease control. They should continue daily emollient and soap substitute use. After several months patients should try stopping topical steroids (continuing emollients and soap substitutes). Patients using maintenance treatment should be reviewed every 3-6 months to check for treatment response and signs of cutaneous atrophy. |
| Topical treatment failure? | When to refer:Doesn’t respond to suggested potency of topical steroidCan’t reduce frequency of application to twice weekly maintenance without eczema flaringCan’t stop maintenance treatment after several months without eczema flaring |
Topical steroid side effects
- Some patients find topical steroids can cause burning or stinging on initial application, particularly if skin is very inflamed. This usually improves with continued use.
- cutaneous atrophy – particularly in delicate sites, with prolonged use
- Skin looks red, bruises easily, has more visible subcutaneous blood vessels and/or telangiectasia
- If detected early, changes may be reversible
- Permanent striae.
- Acne vulgaris/perioral dermatitis/rosacea.
Topical calcineurin Inhibitors
- Provide information leaflet (see Resources section).
- They can be initiated in primary care if the GP is comfortable to do so, where eczema is uncomplicated and topical corticosteroid usage has not given sustained benefit or is considered likely to cause adverse effects. Please seek advice from the department if you would like support with initiating this treatment.
- Tacrolimus 0.1% and 0.03% ointment is licensed for treatment of moderate to severe atopic eczema .
- Pimecrolimus cream is licensed for treatment of mild to moderate atopic eczema.
- Apply to areas of active eczema twice daily for up to 3 weeks, and then once daily thereafter if eczema still active.
- Apply just enough to produce a shine on treated skin.
- Caveats:
(1) Do not apply to skin that is infected
(2) Sun-protect treated areas
(3) Avoid applying emollient within 2 hours of applying tacrolimus (SPC advice).
- Warn patients and carers that it may sting on initial application, but that this tends to diminish over 3-4 days with continued use.
- Review the amount prescribed at least twice a year.
- Review treatment every 2-3 months.
Recognising bacterially infected eczema
- Many patients with atopic eczema will be chronically colonised with staphylococcus aureus. There is no clear evidence that reducing chronic bacterial colonisation improves eczema control. However, weeping, pustules, crusts, eczema not getting better or rapidly worsening, fever and malaise suggest significant infection which requires treatment with antibiotics
- Take a bacterial swab (resistance is not uncommon), treat with oral antibiotics or combined topical antibiotic/steroid preparations. Fusidic acid preparations are only suitable for short term use due to high resistance rates.
- Remember that antibiotics alone will not usually settle down a flare of atopic eczema – topical steroids and emollients will also be required.
Recognising virally infected eczema (eczema herpeticum)
- Areas of rapidly developing painful eczema, clustered blisters like early stage cold sores, circular punched-out erosions, possible fever and malaise are suggestive of eczema herpeticum. Some patients suffer from repeated episodes.
- Take a viral swab for PCR if possible.
- Stop topical steroids/calcineurin inhibitors.
- Consider starting empirical acyclovir.
- Refer urgently to dermatology registrar on call via NHS Lothian Switchboard.
- Consider need for ophthalmology review if periocular skin is affected.
For Patients
Patient information leaflet – https://www.bad.org.uk/pils/atopic-eczema/
Eczema Outreach Scotland http://www.eos.org.uk/
National Eczema Society http://www.eczema.org/
For Health Professionals
SIGN Guideline 125 on Management of atopic eczema in primary care: https://www.sign.ac.uk/sign-125-management-of-atopic-eczema-in-primary-care.html
Primary Care Dermatology Society: http://www.pcds.org.uk/clinical-guidance/atopic-eczema
Clinical Knowledge Summaries https://cks.nice.org.uk/eczema-atopic
Patient Action Plan – http://www.bristol.ac.uk/primaryhealthcare/researchthemes/apache/ewap/
Finger Tip Units – information can be found on CKS site above and at https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/topical-steroids/













