The Scottish Cancer Referral Guidelines have been updated and went live on Wednesday, 6th August 2025. We are working hard to update all relevant information on the RefHelp website. If you would like to see the guidelines please click here Scottish Referral Guidelines for Suspected Cancer 2025 – gov.scot
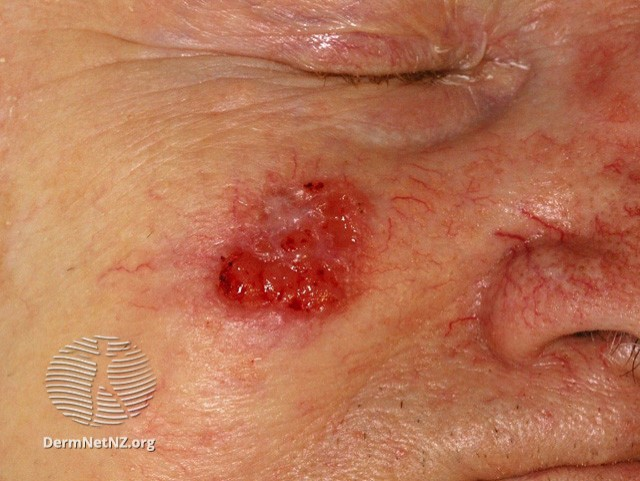
Suspected squamous cell cerinoma (SCC)
SCC Face
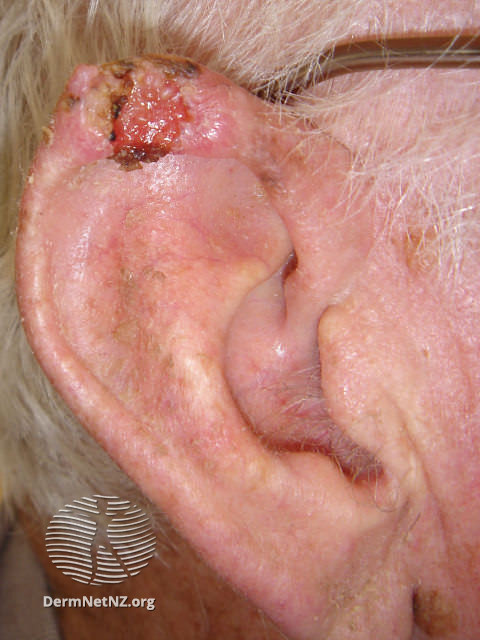
SCC Ear
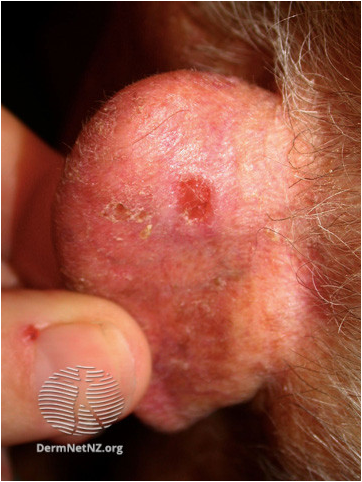
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
BCC Ear
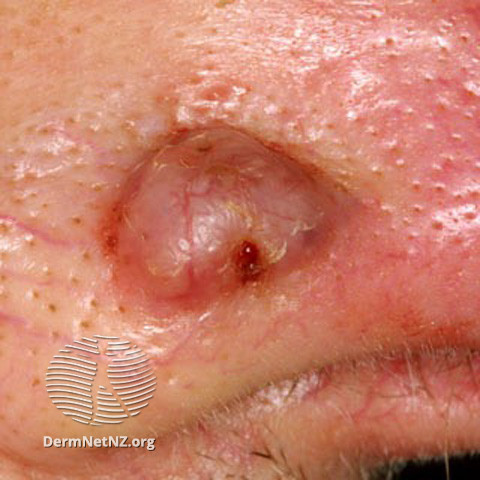
BCC Nose
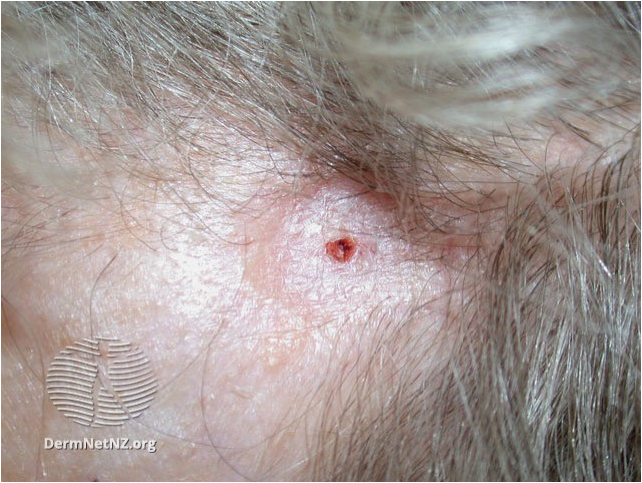
BCC Morpheic
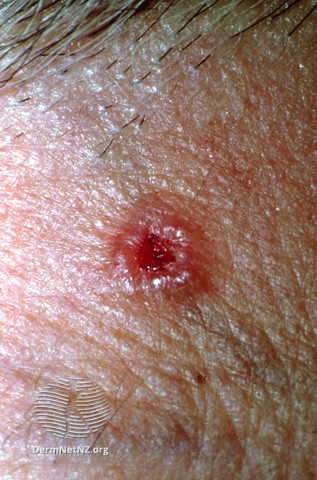
BCC with pearly edge
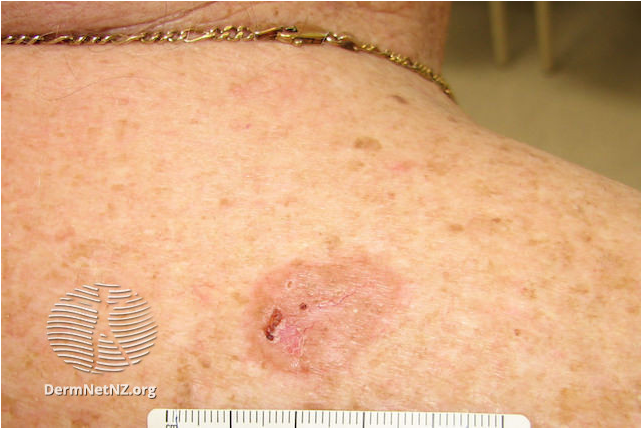
BCC Superficial
Diagnostic Tips
Suspected squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
- Squamous cell carcinoma usually develop on sun-exposed, sun damaged skin
- Men affected more than women especially on bald scalps
- Suspect keratotic nodules with thickened base
- Usually rapid growth compared with basal cell carcinoma
- Metastases occur in 5% of squamous carcinoma
Suspect Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
- Usually slow growth often over several months or years
- Non-healing lesion which may bleed or crust
- Provide education on sun avoidance and photoprotection
- The risk of developing another BCC is high (40% over 5 years)
High Risk Squamous Cell Carcinoma
More likely if:
- Long term immunosuppression
- High risk sites, e.g. lips, ears and in scars
- Rapidly growing tumour
All images on this page have been sourced from Search DermNet | DermNet (dermnetnz.org)
R.C 25-04-24
Dermatology Referral Criteria
Criteria for referral-SCC
- All suspected SCC
- SCC excised in primary care should be discussed with local skin cancer MDT
Criteria for referral – BCC
- Any BCC which cannot be managed in Primary Care
- Diagnosis uncertain
- Morphoeic or sclerosing BCC with indistinct margins
- High risk sites e.g. naso-labial
- Cosmetically difficult sites e.g. periorbital
- High risk patients i.e. immunosuppressed
- Patients with multiple tumours
Please use the Consultant Connect app to take photos of the lesion(s) and then attach these to your Sci Gateway referral.
Management
Suspected squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
Refer urgently to dermatology/Plastic surgery as per local pathways.
Suspected basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
Low risk BCC can be removed in primary care where an appropriate service is available.
Criteria for removal in Primary Care (BCC)
- Diagnosis certain
- Well defined margins
- BCC should be excised with a 4 mm lateral margin and a deep margin of 2 – 3 mm and a cuff of fat
- Warn patient about scarring
- Send all specimens to pathology
Link to PCDS squamous-cell-carcinoma guidance
Link to PCDS basal-cell-carcinoma-an-overview guidance
Please use the Consultant Connect app to take photos of the lesion(s) and then attach these to your Sci Gateway referral.













