History
- New onset of persistent localised headache (usually unilateral and in the temporal area, but can be bilateral) in a patient age >50 years.
- Jaw claudication (pain over masseter muscles on chewing)
- Tenderness or pain over scalp.
- Visual disturbance
- Constitutional Symptoms: Malaise, weight loss, unexplained fever, night sweats.
- There may also be symmetrical pain and stiffness affecting the shoulder and pelvic girdle.
Examination
- Often normal
- Occasionally focal tenderness and thickening over temporal artery or pulseless artery.
- Visual field defects or reduced visual acuity.
- Cranial nerve defects
Investigations
- ESR and CRP- almost always elevated.
- Further investigations including temporal and axillary artery ultrasound may be organised by rheumatology following referral. Ultrasound is only useful if done within a week of starting the steroids and therefore the urgency to get the patient in for scanning asap.
The GCA probability scoring system can be used to assess likelihood of GCA based on clinical features:
| GCA Probability Scoring System | ||||
| Age | Points | Symptoms | Points | |
| Age <50 | 0 | Headache | 1 | |
| Age 50-60 | 1 | Polymyalgia | 2 | |
| Age 60-65 | 2 | One constitutional Symptom | 1 | |
| Age >66 | 3 | Two or more constitutional Symptoms | 3 | |
| Sex | Signs | |||
| Male | 1 | Visual signs | 3 | |
| Female | 2 | Temporal artery tender | 1 | |
| Temporal artery thickened | 2 | |||
| Symptom duration | Temporal artery pulse loss | 3 | ||
| >24 weeks | 0 | Other extracranial artery tender | 1 | |
| 12-24 weeks | 1 | Other extracranial artery thickened | 2 | |
| 6-12 weeks | 2 | Other extracranial artery pulse loss | 3 | |
| <6 weeks | 3 | Cranial nerve palsy | 3 | |
| CRP | ||||
| <5 mg/L | 0 | Other potential cause | ||
| 6-10 mg/L | 1 | Infection, cancer, other pathology | -3 | |
| 11-25 mg/L | 2 | |||
| >25 mg/L | 3 | |||
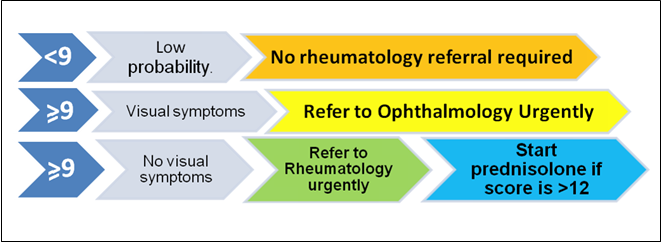
Interpretation: If the score is <9, then probability of GCA is low and referral is not required. If the score is 9 or greater then refer urgently to rheumatology for further investigations. Oral prednisolone 40mg daily should be commenced in primary care in those with a score of>12, pending review at the rheumatology clinic. Prednisolone should not be started in those with a score between 9 and 12.
Interpretation of GCA probability scoring
M.A & H.B/S.R 15-10-24
Please See the Primary Care Management Section for immediate management.
REFER TO OPHTHALMOLOGY URGENTLY IF VISUAL SYMPTOMS PRESENT
NO VISUAL SYMPTOMS- REFER TO RHEUMATOLOGY ONCALL URGENTLY by contacting the Rheumatology on-call registrar through switch board (0131-537-1000).
Please do not refer via Sci Gateway alone.
If for any reason it is not possible to reach the on-call team by phone, please email Rheumatology.oncall@nhslothian.scot.nhs.uk using the header “possible GCA – urgent”. This is not ideal as it may still delay ultrasound scanning and review.
Immediate management
In a patient suspected to have GCA with a probability score of 9 or greater, do the following:
Tests
- Check FBC, U&E, LFT, CRP, ESR
- Check HbA1c (if starting prednisolone).
Steroids
- Start steroid if visual symptoms present –Prednisolone 60mgs
- If no visual symptoms then start steroids only if GCA probability score is >12 Prednisolone 40mg; 60mg if jaw claudication present
- Warn patient about symptoms of hyperglycaemia.
- If HbA1c > 42 , refer to Management of long term high dose steroid therapy – RefHelp (nhslothian.scot)
If the diagnosis of GCA is correct, symptoms should have improved markedly within a week and inflammatory markers should start falling.
Long term management
Steroid dose reduction
Gradually reduce the Prednisolone doseas guided by the Rheumatologist. Typically, we advise that prednisolone should be continued at the starting dose until symptoms have improved and inflammatory markers have returned to normal (usually 2-4 weeks). Thereafter the daily dose of prednisolone should be reduced by 10mg every 2 weeks until the patient is on 20mg daily. Then reduce the dose by 2.5mg every 2-4 weeks until the patient is on 10mg daily, then reduce by 1mg every 1-2 months. When the patient reaches a dose of 4mg daily, check a morning serum cortisol before reducing further. If cortisol is >425nmol/L, proceed with dose reduction and stop Prednisolone if possible. If cortisol is 275 – 425nmol/l, proceed with dose reduction with sick day dosing of 10mg prednisolone (or seek medical attention if unable to take) as per steroid emergency card for 3 months. If cortisol <275nmol/L continue prednisolone 4mg daily and refer to Endocrinology for further advice.
Vascular risk factors
Patients with GCA who have poor vascular health are highest risk for developing complications of GCA such as blindness or stroke. Traditional vascular risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes and hyperlipidaemia should be addressed and treated appropriately.
Gastroprotection.
Treatment with proton pump inhibitors need not be given routinely but should be considered for people at high risk of gastrointestinal bleeding or dyspepsia. (previous GI bleed, known GORD/peptic ulcer disease, currently on anticoagulants)
Bone protection
Treatment should be commenced with alendronic acid 70mg once a week accompanied by cholecalciferol 800 units daily. Alternatives include Risedronate 35mg once a week or liquid buffered alendronate (Binosto, 70mg weekly). A combined calcium and vitamin D supplement (Accrete D3, 1000/880) is indicated in patients with dietary calcium intake <700mg daily. Dietary calcium intake can be calculated by completion of a simple food frequency questionnaire using a dietary calcium calculator.
All patients should be considered for vitamin D supplements (Colecalciferol 800 u daily) and calcium supplements if their dietary Calcium intake is < 700 mg/day. A DEXA scan should be considered in patients who have a 10-year risk for major osteoporotic fractures of >10 %. Oral bisphosphonate treatment should be commenced pending the results of DEXA.
Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry
It is not necessary to refer patients aged 60 years and above who are starting prednisolone for Dual Energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), since there is a high likelihood they will have osteopenia and qualify for treatment. Instead, prophylactic treatment can be commenced with an oral bisphosphonate and calcium and vitamin D supplements as detailed above. Indications for DEXA in this patient group are:
- Patients under the age of 60 years
- Patients with one severe or two or more moderate vertebral fractures on X-ray (indicated if there is back pain and height loss)
- Patients who are able to come off long term prednisolone, to determine if treatment is still indicated
- Patients who have completed 5 years treatment with an oral bisphosphonate
X-rays
Thoracic and lumbar spine x-rays are indicated in patients with back pain, kyphosis or height loss to confirm of exclude the presence of vertebral fractures.
Recurrence of GCA during steroid dose reduction
If GCA symptoms recur during steroid dose reduction, check ESR/CRP and increased the prednisolone dose to the dose that was last controlling symptoms and contact rheumatology for advice.
Recurrence of GCA with visual symptoms
If a patient with a diagnosis of GCA has a recurrence of headache and visual symptoms, please check ESR and CRP, increase or restart prednisolone to 60mg daily and contact Rheumatology.
Information for patients
Versus Arthritis: https://www.versusarthritis.org/about-arthritis/conditions/giant-cell-arteritis-gca/
Information for health care professionals
British Society for Rheumatology guideline on diagnosis and treatment of giant cell arteritis. https://academic.oup.com/rheumatology/article/59/3/487/5714025
Endocrinology Refhelp page, Information on management of patients on long term steroid therapy













